Method Article
Deep-Tissue Three-Photon Fluorescence Microscopy in Intact Mouse and Zebrafish Brain
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
Three-photon microscopy enables high-contrast fluorescence imaging deep in living biological tissues, such as mouse and zebrafish brains, with high spatiotemporal resolution.
Abstract
Multiphoton microscopy techniques, such as two-photon microscopy (2PM) and three-photon microscopy (3PM), are powerful tools for deep-tissue in vivo imaging with subcellular resolution. 3PM has two major advantages for deep-tissue imaging over 2PM that has been widely used in biology laboratories: (i) longer attenuation length in scattering tissues by employing ~1,300 nm or ~1,700 nm excitation laser; (ii) less background fluorescence generation due to higher-order nonlinear excitation. As a result, 3PM allows high-contrast structural and functional imaging deep within scattering tissues such as intact mouse brain from the cortical layers to the hippocampus and the entire forebrain of adult zebrafish.
Today, laser sources suitable for 3PM are commercially available, enabling the conversion of an existing two-photon (2P) imaging system to a three-photon (3P) system. Additionally, multiple commercial 3P microscopes are available, which makes this technique readily available to biology research laboratories. This paper shows the optimization of a typical 3PM setup, particularly targeting biology groups that already have a 2P setup, and demonstrates intravital 3D imaging in intact mouse and adult zebrafish brains. This protocol covers the full experimental procedure of 3P imaging, including microscope alignment, prechirping of ~1,300 and ~1,700 nm laser pulses, animal preparation, and intravital 3P fluorescence imaging deep in adult zebrafish and mouse brains.
Introduction
In life science, multiphoton microscopy (MPM) techniques, such as 2PM and 3PM, have been powerful tools for deep in vivo imaging with high spatiotemporal resolution and high contrast in scattering tissues. Additionally, these methods cause less photobleaching when compared to one-photon confocal microscopy1,2,3,4. 3PM is advantageous for deeper-tissue imaging when compared to 2PM due to two major features : (i) employment of longer wavelength excitation (~1,300 nm or ~1,700 nm) reduces tissue scattering, and (ii) the higher-order excitation process (i.e., fluorescence signal depends on the cube of the excitation power in 3PM instead of the square of the excitation power in 2PM) that suppresses the unwanted background fluorescence3. Consequently, 3PM enables high-contrast imaging at deeper regions in living tissues such as the hippocampus in an intact adult mouse brain3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 and the entire forebrain of adult zebrafish12, including Ca2+ activity recording and multicolor observations. Moreover, high-contrast images have been obtained with 3PM through the intact skulls of mouse and adult zebrafish12,13.
Today, excitation laser sources suitable for 3P excitation (3PE) at ~1,300 and ~1,700 nm are commercially available. As the laser scanning system is essentially the same for 2PM and 3PM, converting an existing a 2P setup to a 3P setup is possible in biology laboratories with the installation of a commercially available laser for 3PE. The 3P fluorescence signal is dependent on the laser power, pulse duration, laser repetition rate, and numerical aperture (NA) of the objective lens. Assuming a diffraction-limited focus (i.e., the back aperture of the objective lens is overfilled by the excitation beam), Eq (1) describes the time-averaged fluorescence photon flux from the focal volume resulting from 3PE.
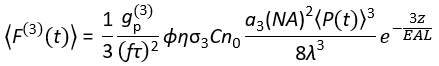 (1)
(1)
Where f is the laser repetition rate, τ is the laser pulse duration (full width at half maximum), ϕ is the system collection efficiency, η is the fluorescence quantum efficiency, σ3 is the 3P absorption cross-section, C is the fluorophore concentration, n0 is the reflective index of the sample medium (e.g., water), λ is the excitation wavelength in vacuum, NA is the numerical aperture of the objective lens, a3 is the spatial integration constant of the focal volume, 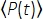 is the time-averaged excitation photon flux (photons/s) under the objective lens, z is the imaged depth, and EAL is the effective attenuation length14. Here we have assumed that the EAL (typically > 100 µm) is much greater than the axial resolution of the microscope (typically < 10 µm). Under paraxial approximation, a3 is equal to 28.114. gp(3) is the 3rd-order temporal coherence of the excitation source, and gp(3) is 0.41 and 0.51 for hyperbolic-secant-squared pulses and gaussian pulses, respectively. The collection efficiency ϕ can be estimated by considering the fluorescence collection by the objective lens, transmittance of the objective lens, the reflectivity of the dichroic mirror, the transmittance of the filters, and the detection efficiency of the detector (e.g., photomultiplier tube, or PMT). As the 3P fluorescence intensity is highly dependent on various parameters, optimization of the 3P setup is required to maximize the 3P fluorescence signals.
is the time-averaged excitation photon flux (photons/s) under the objective lens, z is the imaged depth, and EAL is the effective attenuation length14. Here we have assumed that the EAL (typically > 100 µm) is much greater than the axial resolution of the microscope (typically < 10 µm). Under paraxial approximation, a3 is equal to 28.114. gp(3) is the 3rd-order temporal coherence of the excitation source, and gp(3) is 0.41 and 0.51 for hyperbolic-secant-squared pulses and gaussian pulses, respectively. The collection efficiency ϕ can be estimated by considering the fluorescence collection by the objective lens, transmittance of the objective lens, the reflectivity of the dichroic mirror, the transmittance of the filters, and the detection efficiency of the detector (e.g., photomultiplier tube, or PMT). As the 3P fluorescence intensity is highly dependent on various parameters, optimization of the 3P setup is required to maximize the 3P fluorescence signals.
This protocol illustrates the optimization process of a typical 3P setup, which will be useful particularly for biology laboratories that have a 2P setup and plan to expand its capability to 3P imaging or to maintain their commercial 3P setup at optimal performance. This video article also demonstrates deep-tissue 3P imaging in living animal brains. The first section addresses the optimization of a typical 3P setup with a commercially available laser source and multiphoton microscope. The second and third sections describe zebrafish and mouse preparation, respectively, for 3PM of neuronal structures and activities. The mouse craniotomy surgery has been previously reported in protocol papers as well15,16,17. The fourth section demonstrates intravital 3P imaging in zebrafish and mouse brains.
Protocol
All animal experimentation and housing procedures for zebrafish and mice were approved and conducted in accordance with the Cornell University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) guidance. Zebrafish and mice were euthanized by high-concentration tricaine solution and carbon dioxide asphyxiation, respectively, after the experiment.
1. Optimization of the three-photon microscopy setup
NOTE: Wear laser safety glasses for eye protection. Block the laser beam with a beam blocker when optics are placed or moved. To visualize the laser, use an infrared viewer or an infrared detector card.
- Turn the laser on and set the center wavelength of the idler output of the non-collinear optical parametric amplifier (NOPA) at ~1,300 nm or ~1,700 nm.
- Place a thin cover glass on the beamline from the signal port of NOPA (i.e., ~700-900 nm) to reflect a small fraction of the laser beam to a Si photodiode to obtain triggering signals (Figure 1). Place a beam blocker in the transmission path of the cover glass.
- Place pulse compressors on the light path to prechirp the femtosecond laser to optimize the pulse duration for 3PM. For ~1,300 nm beam, place a prism-pair compressor18,19 (e.g., N-SF11 prism pairs). For ~1,700 nm laser, place a Si plate of ~3 mm in thickness20. Set the angle between the Si plate and the laser path at the Brewster's angle (~73.9° for 1,700 nm) to maximize the laser transmittance. Rotate the Si plate to achieve the Brewster's angle by minimizing the reflection.
- Place flipper mirrors to enable convenient switching between the ~1,300 nm and ~1,700 nm beam lines.
- Place a half waveplate (e.g., an achromatic half waveplate suitable for ~1,300 and ~1,700 nm) mounted on a rotation stage and a polarizing beam splitter (PBS) to control the intensity of the laser. Place a beam blocker in the reflection path of the PBS.
NOTE: The laser needs to pass through the PBS perpendicularly to achieve a high extinction ratio. The laser power for 3PM is controlled by rotating the half waveplate. - Place a thin cover glass in the light path after the power controller and before the optical shutter to reflect a small fraction of the laser beam to a power meter. Use the power meter as a 'reference power meter' to calculate the laser power under the objective during imaging (see step 1.12).
- Align the laser path by adjusting the mirrors to propagate the beam into the 3PM system.
- Measure the beam size at the position of the back aperture of the objective using a knife-edge on a translation stage and a power meter. Ensure that the beam size is not too small or too large.
NOTE: Typically, the beam slightly underfills the high NA objective lens to achieve high power throughput for deep tissue imaging. For example, a beam size of ~10-13 mm (1/e2) at the back aperture of the Olympus objective (~15 mm back aperture diameter) helps achieve an effective NA of ~0.7-0.9. When the beam size is too small, the 3P signal becomes weak, and the spatial resolution worsens because of the low effective NA. When the beam size is too large, the maximum available excitation power under the objective becomes weak due to the power loss at the back aperture of the objective. For deep-tissue imaging, the marginal rays also suffer a higher loss due to the longer path in the tissue. - If the beam size at the back aperture of the objective is not appropriate, place appropriate optical elements, such as convex lenses, in the laser beam path to adjust the beam size.
NOTE: Ensure that the laser beam is not larger than the galvo mirrors to prevent unnecessary power loss. - Place the objective lens on the 3PM setup.
- Measure the pulse duration after the objective using an autocorrelator. Adjust the pulse compressor to achieve shorter pulses if the pulse duration is too long (e.g., >70 fs). Use ~50-70 fs pulses for 3PM and a Michelson interferometer placed between the laser and the objective to provide the delay for autocorrelation measurements.
NOTE: A photodiode with a proper spectral response (e.g., a silicon photodiode for wavelength greater than 1,200 nm) placed at the focus of the objective can conveniently serve as a nonlinear detector, and the two-photon photocurrent from the photodiode can be used to obtain the autocorrelation traces20. The prism-pair compressor for ~1,300 nm can be adjusted in two ways: (1) changing the distance between the two prisms; (2) changing the pathlengths of the laser beam in the prism glass by moving the prism(s) perpendicularly to the baseline of the prism. The Si plate compressor for ~1,700 nm can be adjusted by replacing the Si plate with a thicker or thinner Si plate. - Place a power meter at the output of the objective lens. Measure the laser power under the objective and read the value of the reference power meter (from step 1.6). Calculate the ratio of the power under the objective and at the reference power meter.
NOTE: During imaging, the actual laser power under the objective can be calculated from the power ratio and the value of the reference power meter. - Take out the power meter from under the objective.
- [Optional] Verify photon shot-noise limited performance of the imaging system
NOTE: To perform this task, the following elements are needed: 1) one fluorescein or Texas Red dye pool (e.g., ~10 µM), 2) a photon counter, and 3) an oscilloscope.- Place the dye pool sample under the 3PM objective lens.
- Carefully lower the objective lens onto the dye pool until the distance is less than the working distance of the objective lens.
- Place water between the lens and the cover glass of the dye pool.
- Set the output power of the microscope to a small amount (e.g., <1 mW with ~1 MHz pulse repetition rate) to locate the surface of the dye pool.
- Start the Live session of the microscope and set the z location to zero.
- Slowly move the objective away from the sample to reach the top of the dye pool (as indicated by the third harmonic generation (THG) produced by the cover glass).
- Set the z location to zero at the position of the cover glass.
- Lower the objective slightly until a clear fluorescence signal is visible in the fluorescence channel.
- Connect the output of the PMT to a BNC splitter. Connect the outputs of the divider to the photon counter and the image acquisition system.
- Set the laser power to a value where the photon counts per second are lower than 5% of the laser repetition rate (e.g.,
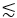 50,000 photons/s when a 1 MHz laser is used).
50,000 photons/s when a 1 MHz laser is used). - Reduce the field of view to the minimum possible with the software and ensure that the brightness is uniform across the image.
- Set the frame rate to 1.0 frame per second.
- Set the acquisition period of the photon counter to t = number of pixels per frame × pixel dwell time and an appropriate discriminator level.
- Collect the photon count and pixel counts simultaneously for an equivalent period. To obtain the pixel count, collect average pixel values of the entire image, as well as the mean and standard deviation values.
- Repeat step 1.14.14, blocking the excitation laser to obtain the dark photon count and pixel counts.
- Stop the Live acquisition of the software.
- Subtract the dark counts (obtained in step 1.14.15) from the photon counts (obtained in step 1.14.14) and the total pixel count (obtained in step 1.14.14).
- Divide the dark-subtracted total pixel count by the dark-subtracted photon count (obtained in step 1.14.17). Use the obtained value as the 'conversion factor' (i.e., pixel values/photon) from a pixel value to a photon count.
- Convert the mean and standard deviation of the pixel counts (obtained in step 1.14.14) to photon counts, i.e., dividing them by the 'conversion factor' (obtained in step 1.14.18). Compare the mean and standard deviation of the photon counts. Ensure that the standard deviation is approximately equal to the square root of the mean of the photon counts if the imaging system performance is close to the shot-noise limit.
- [Optional] Verify the signal detection efficiency of the microscope.
- To test the microscope performance and the signal detection efficiency, follow steps 1.14.1-1.14.17 to obtain photon counts. For step 1.14.15, create a blank sample made of the solvent for the dye and obtain the photon counts for the blank sample with the laser on and at the same power as for the dye pool. Subtract the blank counts from the photon counts from the dye pool to obtain the fluorescence photon counts.
- Use the known 3P cross-sections of fluorescein or Texas Red10,22 and Eq. (1) (with an effective NA to account for the back aperture filling properly) to calculate the expected photon counts and then compare the calculated value with the photon counts measured experimentally. Record both photon counts in the lab notebook as test results for the microscope for future references.
NOTE: Ensure that the calculated and measured values are close to each other (e.g., within a factor of 2). Such quantitative tests of the system are particularly useful to ensure consistent imaging performance over time.
2. Fish preparation for 3PM
NOTE: Wear gloves and a lab coat for this procedure. Choose the adult zebrafish according to the experiment. Finish the entire preparation (steps 2.1 to 2.7) within ~15 min.
- Prepare a Petri dish with ~0.5 cm of 2% high-melting-point agar. Cut a rectangular hole in the agar longer and slightly wider than the fish. Use wax to attach thin tubing (for perfusion of water into the fish's mouth) to the Petri dish with one end in the rectangle. Use wax to attach larger diameter tubing (for removal of water) to the edge of the Petri dish.
- Choose fish for the experiment. Anesthetize the fish with 0.2 mg/mL tricaine solution (pH 7.2) in Hank's solution until the fish is completely unresponsive and deeply anesthetized.
- Place the fish on its side on a wet sponge. Using a microsyringe, retro-orbitally inject 3 µL of pancuronium bromide (0.4 µg/µL in Hank's solution) to paralyze the fish. Place the fish in Hank's solution briefly to ensure it is fully paralyzed.
- Place the fish dorsal side-up in the Petri dish with the head toward the tubing. Using forceps to manipulate the tubing, gently open the fish's mouth and slide the tubing into the mouth. Gently slide the fish toward the tubing so that the tubing will be at the back of the fish's mouth.
- Quickly but gently dry the agar around the fish and remove the water on top of the fish. Dip a small piece of laboratory tissue into laboratory glue and put the tissue onto the agar on both sides of the fish and over the fish's back caudal to the gills.
NOTE: Do not push on the fish or apply pressure. Be careful to avoid getting glue on the gills. - Apply a small drop of bupivacaine directly on the surface of the head to anesthetize the fish during imaging in the region where the laser will be contacting the skin.
- Bring the Petri dish with the fish to the microscope and fill it with fish-facility water. Connect the tubing to a water pump to pump system water at 2 mL/min into the fish's mouth and simultaneously remove the perfusion solution from the dish at the same rate. Ensure that the water is oxygenated with a bubbler and warmed to ~30 °C with an aquarium heater.
NOTE: The fish is now ready for imaging. Monitor the fish's health by monitoring blood flow in the third harmonic generation (THG) signal while imaging (see section 4.1). 3P imaging should also be compatible with more sophisticated fish preparations such as those used in 2P imaging to fix the head and allow body movements while imaging during virtual reality23. This completely non-invasive imaging avoids the need for skull removal as is typical in other studies of vertebrates and is a step toward minimizing invasive research and associated pain.
3. Mouse preparation for 3PM
NOTE: Wear gloves, surgical mask, and lab coat during the following procedures. Choose the mouse line according to the experiment. The mouse should be housed under a 12:12 h light-dark cycle before the surgery. The entire surgery (steps 3.2-3.11) is aseptic, and all surgery tools should be sterilized before use. The craniotomy takes ~1 h.
- Place a donut-shaped (4.5-6.5 mm diameter) coverslip and a coverslip disk (5 mm diameter) on clean parafilm. Use a needle to apply a small amount of optical adhesive to glue the donut-shaped coverslip onto the coverslip disk. Cure the disk-donut coverslip on the parafilm under ultraviolet light for 10-20 min. Remove the entire disk-donut coverslip from the parafilm, and use tweezers to scratch away excess glue and 70% ethanol to remove debris.
NOTE: The coverslips are ~0.17 mm thick. The donut-shaped coverslip is used to apply appropriate pressure on the brain for chronic imaging. - Anesthetize the mouse with 3% isoflurane and 20% O2 gas mixture in an induction chamber. Weigh the mouse. Place the mouse in a prone position on a heating pad. Set the temperature of the heating pad to ~37 °C.
- Fix the upper teeth into the mouth hole of a stereotaxic apparatus with the placement of an anesthetic mask. Fix the ear bars to the ears. Maintain anesthesia with 2% isoflurane and 20% O2 gas mixture during the surgery.
NOTE: Adjust the concentration of isoflurane by monitoring the mouse's response. Check the anesthesia level by watching the breathing rate (~1 Hz for deep sleep) and pinching the feet to check for any reaction before surgery. - Apply eye ointment to the eyes for lubrication. Close the eyelids. Turn on all the surgery lights. Subcutaneously inject ketoprofen, dexamethasone, and glycopyrrolate based on the mouse body weight before surgery.
NOTE: The drug doses are 2 mg/mL, 0.1 mg/mL, and 0.1 mg/mL for ketoprofen, dexamethasone, and glycopyrrolate, respectively. The injection volumes for ketoprofen, dexamethasone, and glycopyrrolate depend on body weight and are 2.5 µL/g, 2 µL/g, and 2 µL/g, respectively. - Remove hair on the crown of the head and near the ears.
- Clip as much hair as possible with scissors or a hair clipper and remove the clipped hair from the surgical site.
- Apply an appropriate amount of depilatory cream. Wait for 1 min.
- Remove hair and cream by using a cotton swab soaked in saline.
- Repeat steps 3.5.2 and 3.5.3 until the hair is completely removed.
- Apply 5% povidone-iodine solution and then 70% ethanol on the skin to cleanse the area. Repeat the process three times.
- Give a subcutaneous injection of atropine (dose based on body weight, 0.02-0.05 mg/kg) on the head. Wait for 1 min.
- Cut the skin on the crown of the head to expose the skull. Ensure the bregma point and the lambda point are both exposed. Glue the remaining skin tissue on the edge to the skull by using biocompatible glue to avoid drilling dust from entering underneath the skin (which may elicit an immune response).
- Use a surgical marker to draw a 5 mm diameter circle over the area of interest. For example, choose the center of the area ~2.5 mm lateral and 2 mm caudal to the bregma, which covers most of the somatosensory cortex and the visual cortex.
- Drill along the circle slowly and apply saline to hydrate the skull when halfway done. Slow the drilling speed for the last half and cover the skull with saline before removing the skull. Open the skull gently with forceps and apply a small piece of sterile gelfoam soaked in saline to immediately stop any bleeding in the brain. Keep the brain hydrated by using saline.
- Apply a drop of saline on the side of the prepared disk-donut coverslip facing the brain tissue. Place the protruded disk part of the disk-donut coverslip into the cranial window. Use a long bar held by the stereotaxic apparatus to gently press the disk part of the coverslip cranial window onto the brain surface, ensuring that the donut part tightly covers the skull. Dry the area around the disk-donut coverslip with a cotton swab.
- Apply a layer of biocompatible glue under the donut-shaped edge. Apply a layer of dental cement mix under and around the donut part of the disk-donut coverslip. Apply another layer of glue above the dental cement. 5% glucose (dose based on body weight, 10 µL/g) can be injected subcutaneously every hour during the surgery to provide animal energy.
- Shut down the anesthesia system. Release the mouse from the stereotactic apparatus. Transfer the mouse to a customized compact stereotactic apparatus immediately, with a heating pad at ~37 °C and an anesthesia apparatus.
- Place the mouse in a prone position on the heating pad of the customized compact stereotaxic apparatus. Set the temperature to ~37 °C. Fix the upper teeth into the mouth hole of the stereotactic apparatus and the ear bars to the ears of the mouse. Put on the anesthetic tubes, and maintain anesthesia with 1.5% isoflurane and 20% O2 gas mixture.
NOTE: The mouse is now ready for imaging. Keep the mouse anesthetized during the following imaging procedures. Adjust the concentration of isoflurane by monitoring the mouse's response.
4. Intravital imaging in fish and mouse brains
- Intravital imaging in the zebrafish brain
NOTE: To properly locate the fish brain under the objective lens, a secondary charge-coupled device (CCD) camera is used on the same path as the excitation light for widefield imaging.- Set up the microscope and calibrate the power (as described in section 1).
- Place a low magnification (typically 4x) objective on the microscope.
- Place the Petri dish containing the fish and the tubes under the microscope.
- Use a light-emitting diode (LED) light source to illuminate the Petri dish.
- Open the Camera mode of the image acquisition software (Figure 2).
- Click Live.
- Choose channel A on the right side of the screen.
- Adjust the histogram settings to see the image clearly.
NOTE: These need to be updated as needed. - Set the motor setting on the motor controller to Base.
- Lower the objective until the fish is visible.
NOTE: Ensure that the objective lens does not make any physical contact with the head. - Place the center of the fish head at the center of the field of view.
- Move the objective up and away from the fish head.
- Replace the low magnification objective lens with the high NA objective lens for 3PM.
NOTE: The low magnification lens and the high NA objective lens do not need to be parfocal but must be close enough to ensure the fish is within the field of view of the high NA objective lens. - Slowly lower the objective lens, ensuring that the objective does not make any physical contact with the head. In the CCD camera software, stop moving the objective when the top of the head is visible. Set the z location to 0 μm.
NOTE: Ensure that there are no air bubbles under the objective lens when using a water-immersion objective. - Turn off the LED light source and close the dark curtain around the system.
- Set the imaging acquisition software to Multiphoton GG mode for 3P imaging and set the power under the objective lens to less than 1 mW (with ~1 MHz pulse repetition rate).
- Change the motor setting button from Base to Objective on the motor controller.
- Turn down the lights in the room.
- Turn on the PMTs and open the 3PM excitation source shutter. Ensure that an outline of the bone appears in the fluorescence signal channel due to autofluorescence and in the THG signal channel due to THG of the bone (Figure 2C).
- Perform imaging at different depths by increasing the power levels when imaging deeper.
- Intravital imaging in the mouse brain
NOTE: Inject 5% glucose into the anesthetized mouse every hour during imaging; the dose is based on body weight (10 µL/g).- Set the imaging acquisition software to Multiphoton GG mode for 3P imaging and set the power under the objective lens to less than 1 mW (with ~1 MHz pulse repetition rate).
NOTE: Ensure that the surgery window is placed perpendicular to the objective lens to reduce aberration. Fine adjustment is performed by tilting the stereotaxic apparatus. - Move the objective lens close to the window and apply water between the objective and the cranial window; set axis values of all motors to zero.
NOTE: Light absorption in H2O at ~1,700 nm is large, which significantly reduces the ~1,700 nm laser power after a depth of ~1-2 mm of water. For ~1,700 nm excitation, use D2O, which has much smaller absorption at 1,700 nm, for water immersion to reduce absorption by water. - Click on the Live button in the image acquisition software and open PMT channels, e.g., one fluorescence signal channel and one THG signal channel. Adjust the PMT gain and background level as needed.
- Slowly move up the objective lens to locate the window surface by monitoring the THG channel from the large blood vessels and the window glass surface. Adjust the window orientation (see the note in step 4.2.12) if needed. Zero the motors to define the surface of the brain.
- Perform imaging and adjust the power level according to the imaging depth.
- Set the imaging acquisition software to Multiphoton GG mode for 3P imaging and set the power under the objective lens to less than 1 mW (with ~1 MHz pulse repetition rate).
Results
The successful completion of this protocol will result in a properly aligned microscope with optimal light parameters (e.g., pulse duration, NA) and animal preparations appropriate for in vivo 3PM. The commercially available 3P setup comprises appropriate mirrors and lenses for both ~1,300 nm and ~1,700 nm; therefore, no change in optics is required when the excitation wavelength is switched between 1,300 nm and 1,700 nm. If the lenses in a 3P setup do not have an appropriate coating for 1,300 and 1,700 nm, these need to be replaced with appropriate ones to reduce laser power loss. With the optimized 3PM and proper animal preparation, in vivo fluorescence and THG images with high contrast can be collected deep within the brains.
Figure 3 shows representative 3P images of intact adult zebrafish. High-resolution, non-invasive, and deep imaging of genetically labeled neurons in the adult zebrafish brain is achieved using 3PM. Although imaging in the telencephalon region has been reported in the adult zebrafish brain using 2PM24,25,26,27, 3PM enables access to the entire telencephalon and regions that are more challenging or impossible to observe using other techniques. The distribution of cell layers in the optic tectum and cerebellum can be observed in Figure 3C. In a successful imaging session, the bone is visible in the THG channel and neurons visible in the fluorescence channel. For adult zebrafish imaging, the camera feature of the microscope was used to locate the fish (Figure 3A). This step is not necessary for mouse brain imaging as the glass window is large enough to make the brain easily accessible. High-resolution structural images of adult zebrafish brain were obtained using the system described in the previous sections. The skull is seen in the THG channel (Figure 3B), which helps navigate the brain and find the top surface. As observed in Figure 3C, neurons are distinguishable with a high signal-to-background ratio (SBR) deep in the adult brain. The tissue above the brain is visible in the fluorescence channel due to autofluorescence.
Figure 4 shows multicolor 3P images of GCaMP6s-labeled neurons (green) and Texas Red-labeled blood vessels (red) together with THG (blue) signals in the adult mouse brain with 1,340 nm excitation10. The images are reproduced from previous work10. In Figure 4, the pulse energy at focus was maintained at ~1.5 nJ in the entire depth to obtain sufficient fluorescence and THG signals, and the maximum average laser power was ~70 mW. The pulse duration was adjusted to ~60 fs, and the effective NA was ~0.8. With optimization of the 3PM setup, high-contrast images were successfully obtained down to 1.2 mm from the brain surface, in the CA1 hippocampus region (Figure 4A,B). Figure 4C,D show Ca2+ activity traces of GCaMP6s-labeled neurons at a depth of 750 µm for a 10 min recording session, showing high recording fidelity.
If the excitation laser is misaligned, nonuniformity in signal brightness across the field of view may be observed. Additionally, if the laser parameters, such as the pulse duration, the excitation pulse energy at focus, and the effective NA, are not optimized, the THG image from the fish skull or the craniotomy window of the mouse brain will not be visible and/or requires high excitation pulse energy (e.g., >2 nJ/pulse at focus). Hence, the THG signals at the brain surface can be used as an indicator for an optimized 3PM setup before starting deep-tissue imaging.
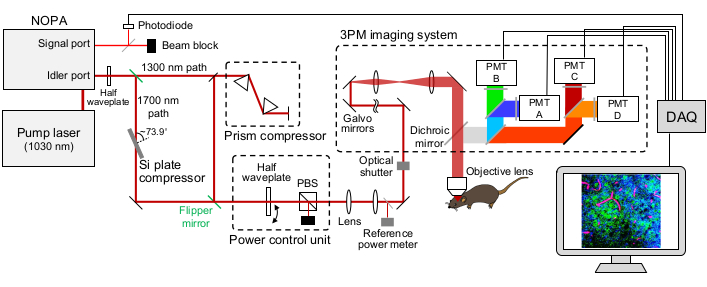
Figure 1: Schematic illustration of a 3PM setup. The wavelength of the excitation laser is set at ~1,300 nm or ~1,700 nm, output from the idler port of the NOPA. The prism-pair compressor and the Si plate compressor are used for the ~1,300 nm and ~1,700 nm laser, respectively, to prechirp the excitation laser pulse. The ~1,300 nm and ~1,700 nm laser beams can be switched with flipper mirrors. The signal port of the NOPA is used to obtain the triggering signal. A half waveplate and a PBS are used to control the excitation power. The fluorescence and THG are detected by GaAsP PMTs. Appropriate combinations of dichroic mirrors and bandpass filters are used to separate the fluorescence and THG signals. Abbreviations: 3PM = three-photon microscopy; NOPA = non-collinear optical parametric amplifier; PBS = polarizing beam splitter; THG = third-harmonic generation; DAQ = data acquisition; PMT = photomultiplier tube. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
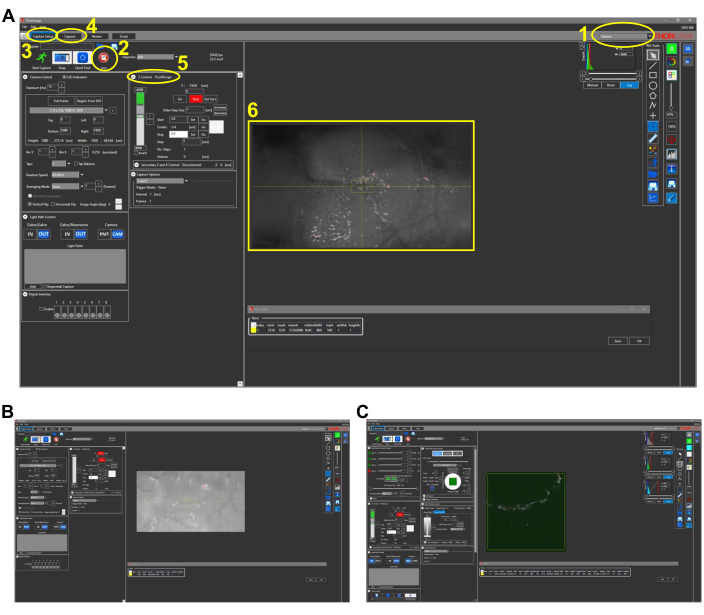
Figure 2: Representative screenshots for intravital Imaging in fish (protocol section 4.1). (A) Camera mode view of the image acquisition software with 4x objective lens in place. Key features of the software are outlined and numbered as follows: 1. Imaging mode of the image acquisition software. The mode options are Camera, Multiphoton, and Multiphoton GG. For white light imaging with CCD camera, the Camera mode is chosen. 2. Clicking the Live button turns on the camera (or PMTs if in multiphoton options), and a real-time view of the microscope can be observed. 3. In Capture Setup tab, the desired imaging parameters (power, location, depth) are set. 4. In Capture tab, a folder location is assigned for the images to be saved. The imaging can be started in this tab. 5. The Z Control setting controls the depth of imaging by moving the z stage motor. 6. Representative image of a zebrafish head. The rostral side of the head is on the left. (B) Representative view of Camera mode with 25x objective lens. (C) Representative view of Multiphoton GG mode containing the THG image of image seen in (B). Abbreviations: CCD = charge-coupled device; PMT = photomultiplier tube; THG = third-harmonic generation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
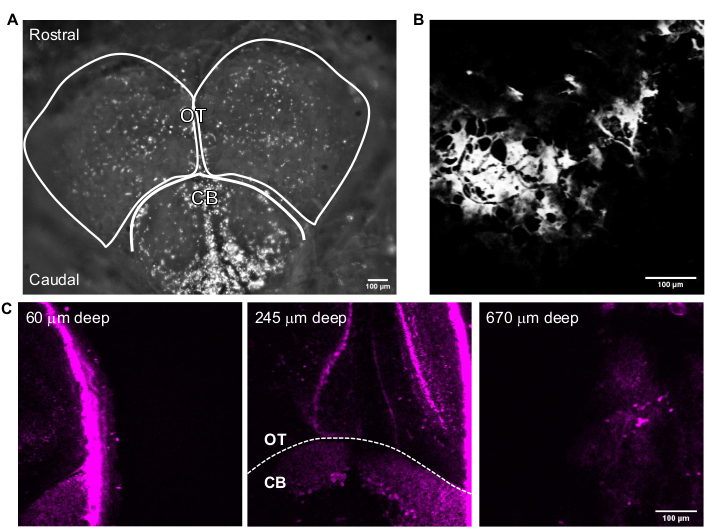
Figure 3: Representative images of the adult zebrafish brain acquired with the image acquisition software. (A) Camera mode image of adult zebrafish head acquired with a 4x objective lens. The top of the image is the rostral direction. The OT lobes and CB are outlined. (B) Representative image acquired in Multiphoton GG mode with a 25x objective lens containing the THG image of (A). (C) Fluorescence images of adult zebrafish brain at the intersection of the cerebellum and the optic tectum where GFP is expressed in cytoplasm of neurons in various depths. Scale bars = 100 µm. Abbreviations: OT = optic tectam; CB = cerebellum; THG = third-harmonic generation; GFP = green fluorescent protein. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
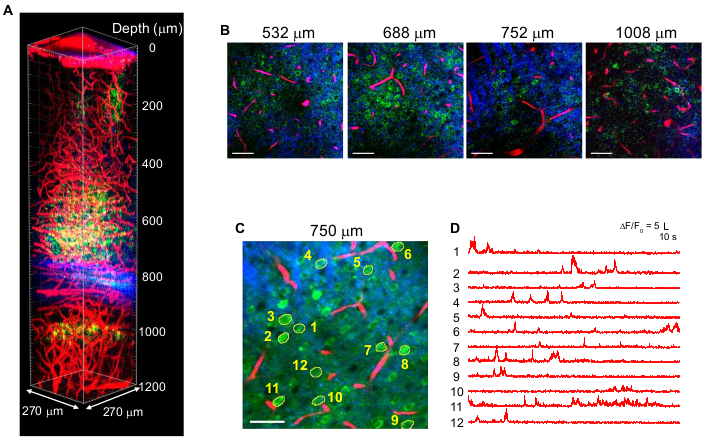
Figure 4: Multicolor 3PM of GCaMP6s-labeled neurons (green), Texas Red-labeled blood vessels (red), and third-harmonic generation (blue) upon 1,340 nm excitation in the mouse brain. (A) Z-stack images down to 1,200 µm from the brain surface with a field-of-view of 270 x 270 µm (512 x 512 pixels per frame). The laser power was varied according to the imaging depth to maintain ~1.5 nJ pulse energy at the focus. Maximum average power under the objective was 70 mW. (B) Selected 2D images at various imaging depths. (C) Activity recording site at 750 µm beneath the dura with a field-of-view of 270 x 270 µm (256 x 256 pixels). (D) Spontaneous brain activity traces recorded in an awake mouse from the labeled neurons indicated in (C). The frame rate was 8.3 Hz, with a pixel dwell time of 0.51 µs. The laser repetition rate was 2 MHz, and the average power under the objective lens was 56 mW. Each trace was normalized to its baseline and low-pass filtered using a hamming window of 0.72 s time constant. Scale bars = 50 µm. This figure and the figure legend are reproduced from 10. Abbreviation: 3PM = three-photon microscopy. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
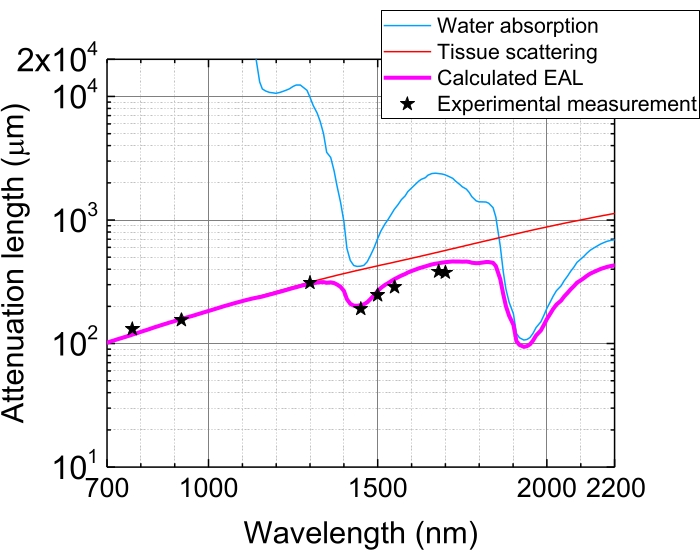
Figure 5: Effective attenuation length in the neocortex of the mouse brain. EAL (magenta line) is calculated from the tissue scattering (red line) and the water absorption in the tissue (blue line), assuming 75% water composition. The black stars indicate reported experimental data of EAL in the neocortex of the mouse brain3,21,28,29. Note that EAL varies in different tissues. Abbreviation: EAL = effective attenuation length. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
| Excitation wavelength (nm) | Immersion water | Maximum laser power (mW) | Maximum pulse energy at focus* (nJ) | Typical EAL in the mouse cortex (µm) | Imaging depth in the mouse cortex** (mm) | Pulse energy under the objective*** (nJ) | Maximum laser repetition rate**** (MHz) |
| 1300 | H2O or D2O | 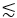 100 100 | 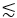 2 2 | ~300 | 0.8 | ~14 | ~7 |
| 1.2 | ~55 | ~2 | |||||
| 1.6 | ~210 | ~0.5 | |||||
| 2.1 | ~1100 | ~0.1 | |||||
| 1700 | D2O | 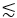 50 50 | 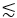 3 3 | ~400 | 0.8 | ~7 | ~7 |
| 1.2 | ~20 | ~2.5 | |||||
| 1.6 | ~55 | ~1 | |||||
| 2.1 | ~190 | ~0.3 |
Table 1: Typical 3P excitation conditions for mouse cortex imaging.
*With a high NA (~1.0) objective, pulse width of ~50 fs, and typical fluorophores such as fluorescent proteins (e.g., GFP and RFP).
** With the assumption that the EAL is uniform in the entire cortex.
*** To achieve ~1 nJ/pulse at focus, calculated from the EAL and the imaging depth.
**** Calculated from the pulse energy under the objective and the maximum permissive laser power.
Abbreviations: 3P = three-photon; NA = numerical aperture; GFP = green fluorescent protein; RFP = red fluorescent protein; EAL = effective attenuation length.
Discussion
This protocol explains step-by-step procedures for setting up 3P imaging with a commercial microscope and laser source. Compared to 2PM, 3PM has an advantage in applications requiring optical access in the deeper regions such as in the mouse brain hippocampus. Although 3PM is mostly used in neuroscience, 3PM can be potentially applied in other tissues such as lymph nodes, bones, and tumors for deep-tissue observation.
It is important to verify that the imaging system performs at close to the shot-noise limit, which ensures that the detection and data acquisition electronics contribute negligible noise to the image after the PMTs. The uncertainty in the number of photons detected is fundamentally limited by photon shot noise. Shot-noise limited performance can be achieved in a typical multiphoton microscope using a high-gain photodetector (e.g., a PMT). Photon shot noise follows a Poisson statistical distribution, wherein the standard deviation of the distribution is equal to the square root of the mean of the distribution. To verify the shot-noise limited performance, follow step 1.14 in the protocol section.
To avoid light attenuation by H2O, using D2O for immersion is helpful, particularly for ~1,700 nm excitation. When D2O is used, it is essential to refresh D2O every ~10 min or use a large volume of D2O to avoid D2O/H2O exchange during imaging. One can also seal the D2O from the room environment3. If a long working distance (WD) objective lens (e.g., WD at 4 mm or longer) is used for imaging, the immersion liquid thickness can exceed 2-3 mm. The increased thickness makes H2O absorption non-negligible even at ~1,300 nm21. Therefore, D2O may be necessary even for 1,300 nm 3PM when using a long WD objective lens.
As the 3P fluorescence intensity depends on the cube of the excitation pulse energy at the focus (Eq. (1)), setting the appropriate laser power is particularly important to obtain adequate 3P fluorescence signals while avoiding thermal and nonlinear damage in living tissues. The average laser power should be kept below the thermal damage threshold. In the mouse brain, for example, to avoid thermal tissue damage, the average power on the mouse brain surface should be kept at or below ~100 mW for ~1,300 nm excitation at a depth of 1 mm and with a field-of-view (FOV) of 230 µm x 230 µm21. Similarly, the average power at ~1,700 nm should be kept at or below ~50 mW at ~1 mm depth and a FOV of ~230 µm x 230 µm (unpublished data). Further, to avoid excitation saturation and potential nonlinear damage, the excitation pulse energy should be kept at 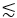 2 nJ and
2 nJ and 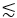 3 nJ for ~1,300 nm and ~1,700 nm excitation, respectively30.
3 nJ for ~1,300 nm and ~1,700 nm excitation, respectively30.
Due to light absorption and scattering in tissues, the pulse energy at focus is attenuated to 1/e (~37%) after penetration of tissues by 1 EAL. The EAL varies in different tissues and with the excitation wavelengths, e.g., in the neocortex of the mouse brain, the EAL is ~300 µm and ~400 µm at ~1,300 nm and ~1,700 nm, respectively3,29 (Figure 5). Therefore, to keep the same pulse energy at focus (e.g., 1 nJ/pulse) at a depth of n EALs, the surface pulse energy needs to be multiplied by 1 nJ × en. For fast imaging of structural and functional dynamics, an excitation laser with a high repetition rate (at 1 MHz or higher) is desirable to achieve a high frame rate5,6,7,10. However, the pulse energy requirement and the average laser power limit constrain the applicable repetition rate.
For example, when we image a moderately deep region at 4 EALs (i.e., ~1.2 mm in the mouse cortex with 1,300 nm excitation), ~55 nJ/pulse at the surface is required to keep 1 nJ/pulse at focus. When the average power limitation is 100 mW, we can apply a ~2 MHz laser repetition rate. However, to image deeper at a depth of 7 EALs, ~1,100 nJ/pulse is required at the surface to maintain 1 nJ/pulse at focus. Assuming the maximum average power is 100 mW to avoid thermal damage, the laser repetition rate should be reduced to 0.1 MHz to achieve a 1,100 nJ/pulse at the surface. Table 1 summarizes typical imaging conditions in the mouse brain cortex. Note that the imaging depths in Table 1 assume that the EAL is uniform in the entire mouse cortex.
Moreover, because of the laser power limitation in deep-tissue 3PM, a trade-off exists between the frame rate and the image pixel size, which is particularly important for functional imaging such as calcium imaging. The maximum available laser repetition rate is decided at each depth based on the required pulse energy at focus and the applicable average laser power as discussed above, e.g., 2 MHz at a depth equivalent to ~4 EALs with 1,300 nm excitation. In general, imaging requires at least one pulse per pixel. Accordingly, the minimum available pixel dwell time is determined by the laser repetition rate, e.g., 0.5 µs/pixel with 2 MHz excitation.
To keep the high spatial resolution (~1 µm in lateral) in 3P images, it is ideal to set 1 pixel to an area of ~1 µm2, e.g., 256 x 256 pixels for a FOV of 250 x 250 µm2. Hence, to perform fast imaging with a considerably large FOV (e.g., 250 x 250 µm2 with 256 x 256 pixels), 0.5 MHz, 1 MHz, and 2 MHz pulse repetition rates give theoretical maximum frame rates of ~7.6, ~15, and ~30 frames/s, respectively. Likewise, the optimization of the laser repetition rate is essential, depending on the target depth, scan speed, and FOV, to apply adequate pulse energy under the thermal damage threshold. To increase the imaging speed, an adaptive excitation source can be used to concentrate all the excitation pulses on the neurons (i.e., regions of interest) by delivering laser pulses on demand to the neurons31.
3PM is advantageous when compared to 2PM in deep imaging within living tissues and through highly scattering media such as a skull, bones, and the white matter layer (i.e., the external capsule) of the mouse brain. The longer EAL and the higher-order nonlinear excitation of 3PE benefits deep-tissue imaging. For example, to image GCaMP6 in the mouse cortex, 2P fluorescence signal with 920 nm excitation is higher than 3P fluorescence signal with 1,300 nm excitation in shallow regions at 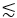 690 µm (i.e., ~2.3 EALs at 1,300 nm)21. However, due to the longer EAL at 1,300 nm compared to 920 nm, 3PE gives stronger fluorescence than 2P excitation (2PE) at a depth of ~690 µm and deeper21. This depth is defined as 'signal crossover depth,' at which the fluorescence signal strengths of 2PE and 3PE are identical with the same repetition rate and the same maximum allowable average powers21. The signal crossover depth depends on the excitation wavelengths for 2PE and 3PE and the fluorophore.
690 µm (i.e., ~2.3 EALs at 1,300 nm)21. However, due to the longer EAL at 1,300 nm compared to 920 nm, 3PE gives stronger fluorescence than 2P excitation (2PE) at a depth of ~690 µm and deeper21. This depth is defined as 'signal crossover depth,' at which the fluorescence signal strengths of 2PE and 3PE are identical with the same repetition rate and the same maximum allowable average powers21. The signal crossover depth depends on the excitation wavelengths for 2PE and 3PE and the fluorophore.
In practice, 920 nm excitation allows higher average laser power than 1,300 nm excitation due to less water absorption. However, the higher average power of 2PE would push the signal crossover depth only by 0.9 EALs4. In addition, when the sample is densely labeled, 3PE has the additional advantage of much higher SBR. Therefore, even before reaching the signal crossover length, 3PM can be better for imaging than 2PM. For example, when imaging the mouse brain vasculature, which has a volume fraction (i.e., labeling density) of ~2%, 1,300 nm 3PM with 100 mW excitation power outperforms 920 nm 2PM with 200 mW excitation power at a depth of ~700 µm for fluorescein.
3PM also has an advantage when imaging through a thin but highly scattering layer that may distort the point-spread function of the excitation beam and generate a defocus background4. For example, through the intact skull of the mouse brain, 2PM images suffer from the defocus background even at the shallow depth of <100 µm from the brain surface13. A similar defocus background was observed in 2PM with 1,280 nm excitation through the white matter in the mouse brain32. Therefore, when tissues are imaged through turbid layers, 3PM is preferable to 2PM for high-contrast imaging regardless of the labeling density.
We recently reported a beads phantom and theoretical analysis showing that the imaging depth limit of 3PM is over 8 EALs33; 8 EALs are equivalent to ~3 mm with ~1,700 nm excitation in the mouse cortex. However, the currently available laser does not have enough pulse energy to achieve 8 EALs in the mouse brain. Further development of stronger lasers will push the current imaging depth limit of 3PM.
Disclosures
The authors declare no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSF DBI-1707312 Cornell NeuroNex Hub and NIH 1U01NS103516.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 5% Povidone-iodine | Amazon | NDC 67818-155-32 | Aceptical cleaning of surgical areas |
| 70% Ethanol | Thermo Fisher Scientific | CAS 64-17-5 | Aceptical cleaning of surgical areas |
| Agarose | Sigma | A4718-256 | Preparing zebrafish chamber |
| Atropine | Cornell Veterinary Care | ||
| Bergamo II | Thorlabs | Multiphoton Imaging Microscope | |
| Bupivacaine | Cornell Veterinary Care | ||
| Dexamethasone | Cornell Veterinary Care | ||
| Donut shape glass (ID4.5, OD6.5) | Potomac Photonics | Cover glass used for craniotomy | |
| eye ointment (or topical ophthalmic ointment) | Puralube Vet Ointment | NDC 17033-211-38 | Used as a lubricant to prevent irritation or to relieve dryness of the eye during surgery and anesthesia |
| GaAsP Amplified PMT | Thorlabs | PMT2100 | PMT detector |
| Glucose | Cornell Veterinary Care | ||
| Glycopyrrolate | Cornell Veterinary Care | ||
| Heater (800 W) | Finnex | Aquarium heater for zebrafish water) | |
| Isoflurane USP 250 mL | Piramal | NDC 66794-0013-25 | For anesthesia of mice |
| Ketoprofen | Cornell Veterinary Care | ||
| Kimwipes | Kimtech | Laboratory tissue for preparing zebrafish | |
| Nanofil syringe (10 micrometer) with 36 G needle | WPI | NANOFIL + NF36BV | Syringe and needle for injection of pancuronium bromide |
| Optical Adhesive | Norland | NOA 68 | To stick round coverslip and donut shape glass together. |
| Pancuronium Bromide | Cornell Veterinary Care | ||
| Peristaltic Pump | Elemental Science | ESI MP2 | Water pump for zebrafish setup |
| Polyethylene tubing (I.D. 0.58 mm., O.D. 0.965 mm.) | Elemental Science | MP2 pump tubing | Tubing that goes in the mouth of the zebrafish |
| Round Cover Slip German Glass #1.5, 5 mm | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 7229605 | Cover glass used for craniotomy |
| Spirit-NOPA | Spectra Physics | Tunable Optical Parametric Amplifier | |
| SR400 | Stanford Research Systems | SR400 | Photon counter |
| Standard Photodiode Power Sensor | Thorlabs | S122C | Power detector |
| Sterilized phosphate buffered saline (PBS) | Millipore Sigma | SKU 806552-500ml | Used during mouse brain surgery |
| Surgical drape | Dynarex disposable towel drape | 4410 | For aceptical mouse surgery |
| Thin strip boxing wax | Corning Rubber Co., Inc. | Holding tubing in place in zebrafish chamber | |
| ThorImage | Thorlabs | Image acquisition software | |
| Tricaine (Ethyl-m-aminobenzoate methanesulfonate salt) | MP | 103106 | Zebrafish anesthesia and euthanasia |
| Tygon tubing (I.D. 1/16 in., O.D. 1/8 in.) | Tygon | Tubing for water flow for zebrafish preparation | |
| VaporGuard | VetEquip | 931401 | For recycling isoflurane |
| Vetbond tissue adhesive | 3M | 1469SB | To glue the glass window on the mouse skull, and to glue the laboratory tissue when preparing the fish. |
| XLPLN25XWMP2 | Olympus | Multiphoton Excitation Dedicated Objective |
References
- Denk, W., Strickler, J. H., Webb, W. W. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science. 248 (4951), 73-76 (1990).
- Helmchen, F., Denk, W. Deep tissue two-photon microscopy. Nature Methods. 2 (12), 932-940 (2005).
- Horton, N. G., et al. In vivo three-photon microscopy of subcortical structures within an intact mouse brain. Nature Photonics. 7 (3), 205-209 (2013).
- Wang, T., Xu, C. Three-photon neuronal imaging in deep mouse brain. Optica. 7 (8), 947-960 (2020).
- Ouzounov, D. G., et al. In vivo three-photon imaging of activity of GCaMP6-labeled neurons deep in intact mouse brain. Nature Methods. 14 (4), 388-390 (2017).
- Weisenburger, S., et al. Volumetric Ca2+ imaging in the mouse brain using hybrid multiplexed sculpted light microscopy. Cell. 177 (4), 1050-1066 (2019).
- Yildirim, M., Sugihara, H., So, P. T. C., Sur, M. Functional imaging of visual cortical layers and subplate in awake mice with optimized three-photon microscopy. Nature Communications. 10, 177 (2019).
- Takasaki, K., Abbasi-Asl, R., Waters, J. Superficial bound of the depth limit of two-photon imaging in mouse brain. eNeuro. 7 (1), (2020).
- Guesmi, K., et al. Dual-color deep-tissue three-photon microscopy with a multiband infrared laser. Light, Science & Applications. 7, 12 (2018).
- Hontani, Y., Xia, F., Xu, C. Multicolor three-photon fluorescence imaging with single-wavelength excitation deep in mouse brain. Science Advances. 7 (12), 3531 (2021).
- Liu, H., et al. In vivo deep-brain structural and hemodynamic multiphoton microscopy enabled by quantum dots. Nano Letters. 19 (8), 5260-5265 (2019).
- Chow, D. M., et al. Deep three-photon imaging of the brain in intact adult zebrafish. Nature Methods. 17 (6), 605-608 (2020).
- Wang, T., et al. Three-photon imaging of mouse brain structure and function through the intact skull. Nature Methods. 15 (10), 789-792 (2018).
- Xu, C., Webb, W. W. Multiphoton excitation of molecular fluorophores and nonlinear laser microscopy. Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy. 5. , 471-540 (2002).
- Mostany, R., Portera-Cailliau, C. A craniotomy surgery procedure for chronic brain imaging. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (12), e680 (2008).
- Łukasiewicz, K., Robacha, M., Bożycki, &. #. 3. 2. 1. ;., Radwanska, K., Czajkowski, R. Simultaneous two-photon in vivo imaging of synaptic inputs and postsynaptic targets in the mouse retrosplenial cortex. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (109), e53528 (2016).
- Kyweriga, M., Sun, J., Wang, S., Kline, R., Mohajerani, M. H. A large lateral craniotomy procedure for mesoscale wide-field optical imaging of brain activity. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (123), e52642 (2017).
- Gordon, J. P., Martinez, O. E., Fork, R. L. Negative dispersion using pairs of prisms. Optics Letters. 9 (5), 150-152 (1984).
- Entenberg, D., et al. Setup and use of a two-laser multiphoton microscope for multichannel intravital fluorescence imaging. Nature Protocols. 6 (10), 1500-1520 (2011).
- Horton, N. G., Xu, C. Dispersion compensation in three-photon fluorescence microscopy at 1,700 nm. Biomedical Optics Express. 6 (4), 1392-1397 (2015).
- Wang, T., et al. Quantitative analysis of 1300-nm three-photon calcium imaging in the mouse brain. eLife. 9, 53205 (2020).
- Cheng, L. -. C., Horton, N. G., Wang, K., Chen, S. -. J., Xu, C. Measurements of multiphoton action cross sections for multiphoton microscopy. Biomedical Optics Express. 5 (10), 3427-3433 (2014).
- Huang, K. -. H., et al. A virtual reality system to analyze neural activity and behavior in adult zebrafish. Nature Methods. 17 (3), 343-351 (2020).
- Jacobson, G. A., Rupprecht, P., Friedrich, R. W. Experience-dependent plasticity of odor representations in the telencephalon of zebrafish. Current Biology. 28 (1), 1-14 (2018).
- Li, J., et al. Early development of functional spatial maps in the zebrafish olfactory bulb. Journal of Neuroscience. 25 (24), 5784-5795 (2005).
- Barbosa, J. S., et al. Live imaging of adult neural stem cell behavior in the intact and injured zebrafish brain. Science. 348 (6236), 789-793 (2015).
- Dray, N., et al. Large-scale live imaging of adult neural stem cells in their endogenous niche. Development. 142 (20), 3592-3600 (2015).
- Kobat, D., et al. Deep tissue multiphoton microscopy using longer wavelength excitation. Optics Express. 17 (16), 13354-13364 (2009).
- Wang, M., Wu, C., Sinefeld, D., Li, B., Xia, F., Xu, C. Comparing the effective attenuation lengths for long wavelength in vivo imaging of the mouse brain. Biomedical Optics Express. 9 (8), 3534-3543 (2018).
- Vogel, A., Noack, J., Hüttman, G., Paltauf, G. Mechanisms of femtosecond laser nanosurgery of cells and tissues. Applied Physics B. 81 (8), 1015-1047 (2005).
- Li, B., Wu, C., Wang, M., Charan, K., Xu, C. An adaptive excitation source for high-speed multiphoton microscopy. Nature Methods. 17 (2), 163-166 (2019).
- Kobat, D., Horton, N. G., Xu, C. In vivo two-photon microscopy to 1.6-mm depth in mouse cortex. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 16 (10), 106014 (2011).
- Akbari, N., Rebec, M. R., Xia, F., Xu, C. Imaging deeper than the transport mean free path with multiphoton microscopy. Biomedical Optics Express. 13, 452-463 (2022).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved