A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Bioluminescent Monitoring of Graft Survival in an Adoptive Transfer Model of Autoimmune Diabetes in Mice
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes a straightforward and minimally invasive method for transplanting and imaging NIT-1 cells in non-obese diabetic (NOD)-severe combined immunodeficient mice challenged with splenocytes purified from spontaneously diabetic NOD mice.
Abstract
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. A promising treatment for this disease is the transplantation of stem cell-derived beta cells. Genetic modifications, however, may be necessary to protect the transplanted cells from persistent autoimmunity. Diabetic mouse models are a useful tool for the preliminary evaluation of strategies to protect transplanted cells from autoimmune attack. Described here is a minimally invasive method for transplanting and imaging cell grafts in an adoptive transfer model of diabetes in mice. In this protocol, cells from the murine pancreatic beta cell line NIT-1 expressing the firefly luciferase transgene luc2 are transplanted subcutaneously into immunodeficient non-obese diabetic (NOD)-severe combined immunodeficient (scid) mice. These mice are simultaneously injected intravenously with splenocytes from spontaneously diabetic NOD mice to transfer autoimmunity. The grafts are imaged at regular intervals via non-invasive bioluminescent imaging to monitor the cell survival. The survival of mutant cells is compared to that of control cells transplanted into the same mouse.
Introduction
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is caused by the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. The loss of beta cell mass results in insulin deficiency and hyperglycemia. T1D patients rely on multiple daily injections of exogenous insulin and experience episodes of severe hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia throughout their lives. The complications related to these episodes include diabetic retinopathy, decreased kidney function, and neuropathy1.
Insulin injections are a treatment but not a cure for T1D. Replacing the lost beta cell mass, however, has the potential to reverse the disease by enabling patients to produce their own insulin. However, the supply of cadaveric donor islets is limited2. Stem cell-derived islets (SC-islets) may provide a virtually unlimited supply of beta cells for transplant. Several groups have demonstrated that human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) can be differentiated to generate functional beta-like cells3,4,5. Promising early clinical trial data indicate that these cells maintain their function following transplant and may enable patients to become insulin-independent6. Chronic immunosuppression is required, however, thus increasing their susceptibility to cancer and infection. In addition, immunosuppressive agents may be cytotoxic to grafts in the long term7. To eliminate the need for immunosuppression, SC-islets may be genetically modified to protect them from recurrent autoimmunity as well as alloimmunity after transplant.
Stem cell research is highly demanding in costs and labor. Mouse cell lines and animal models are useful tools for the initial identification and experimental validation of strategies to protect transplanted cells from autoimmunity. The NOD mouse develops spontaneous autoimmune diabetes with many similarities to human T1D8, and the NIT-1 insulinoma cell line shares a genetic background with this mouse strain9. Diabetes can be adoptively transferred to the related immunodeficient NOD-scid mouse strain via the injection of diabetic splenocytes from NOD mice in order to temporally synchronize the onset of diabetes in replicate experimental mice10. This model can be used to identify genetic targets relatively quickly and inexpensively for further validation in SC-islets. Recently, the method was applied to identify and validate RNLS, a target that was found to protect primary human islets from autoimmunity in vivo and iPSC-derived islets from beta cell stress in vitro11. Described here is a straightforward protocol to transplant genetically engineered NIT-1 cells and non-invasively monitor their survival in an adoptive transfer model of autoimmune diabetes in mice.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
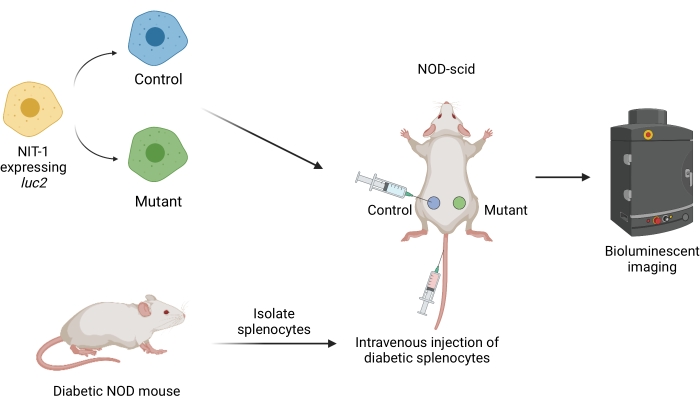
Figure 1: The workflow for transplanting and imaging grafts in an adoptive transfer model of diabetes in mice. NIT-1 cells expressing the firefly transgene luciferase (luc2) are transplanted subcutaneously into NOD-scid mice. The mice are simultaneously injected with autoreactive splenocytes isolated from a spontaneously diabetic NOD mouse. The grafts are imaged at regular intervals by non-invasive bioluminescent imaging. Figure created by BioRender.com. Abbreviations: NOD = non-obese diabetic; scid = severe combined immunodeficient. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
All animal care and study protocols were approved by and performed in accordance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at the Joslin Diabetes Center. NOD and NOD-scid mice may be readily obtained from commercial sources. All mice in this study are maintained in a sentinal-monitored facility. See the Table of Materials for details related to all the materials, animals, instruments, and software used in this protocol.
1. Engineering and maintenance of NIT-1 cell lines
- Maintain NIT-1 cell lines, which share a genetic background with NOD mice, and 293FT cells in tissue culture-treated dishes in DMEM containing 4.5 g/L glucose supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin in a 37 °C incubator with 5% CO2.
- Grow the 293FT cells to 70%-80% confluence for transfection.
- Per 10 cm dish of 293FT cells, combine 10 µg of pLenti-luciferase-blast (see Supplemental File 1), which expresses the firefly luciferase transgene (luc2) under the control of the constitutively active EF1α promotor, 2 µg each of the packaging plasmids pMD2.G, pMDLg/pRRE, and pRSV-Rev, 4 µg of the envelope protein plasmid pCMV-VSV-G, and 60 µg of linear polyethylenimine (PEI) in 1 mL of serum-free DMEM. Adjust the amounts based on the number of cells to be transfected.
- Leave the DNA, PEI, and DMEM at room temperature (RT) for 20 min, and then add them to the 293FT cells.
- Collect the medium containing the lentiviral particles 48 h post transfection.
- Transduce the NIT-1 cells at ~80% confluency with 1 mL of medium containing lentiviral particles per 106 cells for 48-72 h.
- Select the luciferase-expressing cells with 5 µg/mL blasticidin for 48 h.
- Further genetically modify the luciferase-expressing cells to suit the experimental question. Include a luciferase-expressing wild-type or non-targeting control cell line for comparison.
NOTE: Examples of target gene modifications include CRISPR knockout, CRISPRa/i, shRNA knockdown, and overexpression.
2. Preparation of NIT-1 cells for transplant
- Grow the luciferase-expressing cells until they are 80%-90% confluent.
- Remove the growth medium and wash the cells with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, 5 mL for a 10 cm dish).
- Add 1 mL of 0.05% trypsin-EDTA to each dish for 2 min.
- Neutralize the trypsin with 5 mL of growth medium.
- Use a pipette to wash the cells off the dish and transfer them to a conical tube.
NOTE: Cells from multiple dishes of the same cell line can be combined. - Count the cells using a stain such as trypan blue manually with a hemocytometer or automatically with an automatic cell counter.
- Centrifuge at 250 × g for 5 min at RT and remove the supernatant with an aspirating pipette.
- Resuspend the cell pellet in PBS at a concentration of 5 × 107 cells/mL (107 cells per cell line per mouse will be transplanted in a volume of 200 µL).
- Keep the cells on ice (for up to 3 h) until transplantation.
3. Transplantation of NIT-1 cells into NOD-scid mice
- Anesthetize the recipient mice (8-10-week-old NOD-scid mice of the same sex as the mice used to isolate the splenocytes) by isoflurane inhalation in a knockdown chamber. Deliver 2.5% isoflurane into the chamber at a flow rate of 1.5 L/min and an evacuation rate of 9 L/min.
- Lubricate the animal's eyes with ophthalmic ointment to prevent drying.
- Using an electric shaver with a guard, remove the hair from the back (dorsal side) of the mice to expose the skin. The shaved transplant area will be approximately 1 in x 2 in. Return the shaved mice to the knockdown chamber until the transplant.
- Transfer the mice one at a time to a clean surface with an isoflurane nose cone. Gently guide the mouse's head into the nose cone. Use an isoflurane flow rate of 0.25 L/min to maintain the anesthesia during the transplant.
- Wipe the transplant area with an isopropyl alcohol prep pad to remove loose hair and disinfect the skin.
- Ensure the cells are fully resuspended before loading the syringe. Draw an excess volume (>300 µL) of cells into a 1 mL sterile syringe with a 26 G needle. Remove any bubbles; then, return excess cells to the tube so that 300 µL of cell suspension remains in the syringe.
- Using a pair of curved forceps held in the non-dominant hand, gently lift the skin on one side (left or right) of the mouse's back to allow for easier access to the subcutaneous space.
- Using the dominant hand, position the syringe parallel to the coronal and sagittal planes of the mouse's body. With the needle pointed toward the head of the mouse, insert the needle into the skin near the hindquarters, and gently guide it into the subcutaneous space. Ensure that the entire needle remains under the skin and does not poke through.
- Adjust the forceps to gently hold the skin around the base of the needle. Slowly dispense a small amount of cell suspension (<50 µL) and confirm that a small bulge forms under the skin at the site of the injection. Continue injecting the cell suspension until 200 µL has been delivered to the subcutaneous space.
- Holding the forceps in place and keeping the needle parallel to the mouse's body, slowly withdraw the needle. After the needle has been removed, hold the skin closed with forceps for a few seconds to prevent the cells from leaking out of the puncture wound.
- If a genetic modification is being evaluated, repeat the transplant on the opposite side of the mouse using a different syringe so that both mutant and control cells are injected into each mouse, with one cell line on the left and the other on the right. If only one cell line is being transplanted, inject the cells on one side only.
- Following the transplant, transfer each mouse to a fresh cage. Allow each mouse to fully recover from the anesthesia before adding additional mice to the cage.
NOTE: Mice are recovered when they resume normal activities and do not show signs of lethargy or impaired movement. - Evaluate the health status of the mice daily for the duration of the experiment following the transplant. If the grafts form a large bulge or the mice become weak and lethargic, measure their blood glucose and provide 10% (w/w) sucrose water ad libitum to all the hypoglycemic mice. Follow all veterinary recommendations and euthanize any mice with continued poor body condition as per institutional guidelines. In this study, mice were euthanized by CO2 inhalation followed by cervical dislocation.
4. Isolation and purification of autoreactive splenocytes
- Identify 10-16-week-old male or female NOD mice with recent-onset (less than 10 days) diabetes by using urine (or blood) glucose test strips. NOD mice are considered diabetic when they have urine/blood glucose ≥250 mg/dL on at least 2 consecutive days.
NOTE: For each NOD-scid mouse, 10 million splenocytes are needed; one spleen typically yields 50 million to 150 million splenocytes. The splenocytes were isolated from pathogen-free mice housed in a sentinal-monitored facility. - Euthanize the appropriate number of diabetic NOD mice.
NOTE: In this study, the mice were euthanized by CO2 inhalation followed by cervical dislocation to ensure death. - With the mouse on its back, make a vertical incision approximately 2 in in length in the skin with surgical scissors. Open the right side of the mouse from the researcher's point of view and locate the bright red spleen. Gently cut the spleen away from the pink pancreas and transfer it to a sterile 10 cm Petri dish containing 5 mL of sterile PBS. Repeat the dissection with as many mice as needed.
NOTE: Spleens from multiple mice can be combined in one dish. Conduct the following steps using sterile reagents and equipment in a sterile hood. - Mash the spleen(s) with the flat top of a sterile syringe plunger.
- Place a 40 µm or 70 µm strainer in a 50 mL conical tube and wash the strainer with 5 mL of PBS to prime it. Transfer the spleen(s) suspension into the strainer and continue gentle mashing through the strainer. Wash the dish with 10 mL of PBS and transfer the wash to the strainer. Continue mashing until the red color is gone from the strainer.
- Discard the strainer and spin the tube at 500 × g for 5 min at RT. Remove the supernatant with an aspirating pipette.
- Resuspend the cell pellet in 5 mL (for up to three spleens) of ACK lysis buffer prewarmed to RT and lyse the red blood cells for 4 min. Increase the volume by 1-2 mL per spleen if additional spleens are needed.
- Stop the reaction with 5 mL of NIT-1 cell media (described above) per 5 mL of lysis buffer. Pass the cell suspension through a fresh strainer to remove clumps. Discard the strainer, and spin at 500 × g for 5 min at RT.
- Resuspend the cell pellet in 20 mL of PBS, and count the cells. Spin at 500 × g for 5 min at RT. Resuspend the cells in sterile PBS at a concentration of 1 × 108 cells/mL (the injection volume is 0.1 mL/mouse) in a 1.5 mL safe-lock reaction tube.
- Store the cells on ice (for not more than 1 h) or keep the cells at RT, and proceed to the tail vein injection immediately.
5. Intravenous injection of diabetic splenocytes via the lateral tail vein
- Warm up the body of the adult recipient NOD-scid mice (e.g., by using a heat lamp for ~5-10 min) to vasodilate the veins (this helps for visualization and injection into the vein).
NOTE: To avoid the overheating of the mice, do not exceed this time. Always monitor the health status. If the mice appear exhausted or immobile, shut off the heat lamp immediately. - Warm up the cell suspension. Prepare a sterile syringe (0.3-1.0 mL) with a sterile needle (27-30 G, 0.3 mm/0.5 in or smaller), or use a sterile 0.5 mL insulin syringe with a 0.3 mm (0.5 in) needle. Always keep the needle sterile and use a sterile tray if the syringe must be put down between injections.
- Resuspend the splenocyte solution prior to each injection. For each mouse, draw 100 µL of the prewarmed and mixed splenocyte suspension into the syringe. Make sure that no air bubbles are present in the syringe or in the suspension.
NOTE: Make sure to have all the equipment and supplies prepared (alcohol wipes for disinfection, a syringe loaded with the splenocytes to be injected, and a fresh cage for separating injected mice) before placing the mouse in the restraint device. - Place the mouse in the restraint device. Capture the tail with the non-dominant hand and locate one of the two lateral tail veins. Gently rotate the tail if needed. Wipe the tail with a disinfection wipe (70% isopropyl alcohol) to clean the skin and increase the visibility of the vein.
- Insert the needle at an acute angle into the central region of the tail with the dominant hand. With the bevel of the needle facing up, slide the needle a few millimeters through the skin.
NOTE: Make sure the needle is parallel to the vein and placed just slightly under the skin. Be prepared for sudden movements of the mouse/tail directly after penetrating the skin/vessel wall. A successful insertion of the needle should feel like a "smooth slide" into the vein. If another attempt is needed, move further up the tail toward the body. - Apply gentle pressure to the syringe to inject the splenocyte suspension. Do not allow the needle to move further in or out when injecting. Successful injections are smooth without feeling any back pressure during injection and are indicated by a transparent/white blood flow immediately following injection.
- Gently release the needle out of the vein, and apply light pressure to the tail with a disinfection wipe until the bleeding stops. Release the mouse from the restraint device, and gently transfer it to a freshly prepared cage.
NOTE: Inject two to three control mice that do not receive a NIT-1 cell transplant with splenocytes to confirm the potential of the autoreactive splenocytes to induce diabetes, which takes approximately 2-4 weeks post injection.
6. In vivo bioluminescent imaging of NIT-1 grafts
NOTE: Image the grafts one to two times per week. On the day of the transplant, wait at least 2 h after the transplant to allow the grafts to settle and ensure stable luciferase expression. If time is a limiting factor, the initial measurement may be taken on Day 1 instead. A recommended initial imaging schedule is Day 0 or Day 1 post injection, Day 5, Day 10, Day 14, Day 18, and Day 25. Adjust the schedule, however, based on the progress of autoimmunity as judged by the loss of bioluminescent signal.
- Prepare a 15 mg/mL D-luciferin solution in Dulbecco's PBS. Agitate at RT to dissolve, and sterile-filter (0.22 µm). Store 1 mL aliquots at −20 °C, and thaw as needed.
NOTE: The aliquots can be refrozen. - At least 5 min prior to imaging, inject the mice intraperitoneally using a 1 mL syringe and a 26 G needle with D-luciferin solution at a dose of 150 mg/kg.
NOTE: Use a fresh syringe and needle for each mouse. - Anesthetize the mice by isoflurane inhalation according to institutional guidelines. The recommended conditions are 2.5% isoflurane with a flow rate of 1.5 L/min into the knockdown chamber and an evacuation rate of 9 L/min.
- Lubricate the animal's eyes with ophthalmic ointment to prevent drying.
- Open the software associated with the imaging instrument. Create a new user and/or login. On the control panel on the bottom right, select Initialize (Figure 2A). To auto-save the imaging data, create the appropriate folders on the computer, and then select Acquisition | Auto-save to… (Figure 2A). Once the instrument has finished initializing, set the exposure time to 1 min.
NOTE: The complete imaging parameters are shown in Figure 2B. - Transfer the mice one at a time from the knockdown chamber to the imaging instrument. Place the mouse on its stomach with its limbs splayed, and gently guide its head into the nose cone. An isoflurane flow rate of 0.25 L/min delivered via a nose cone is appropriate to maintain anesthesia during imaging. Gently flatten the mouse by pressing the center of its back with both hands and then spreading the hands outward and apart.
- Select Acquire (Figure 2B). Record any relevant details of the experiment in the pop-up window (Figure 2C).
NOTE: See Figure 3A for representative images of three 8-week-old female NOD-scid mice transplanted with two grafts at various time points.
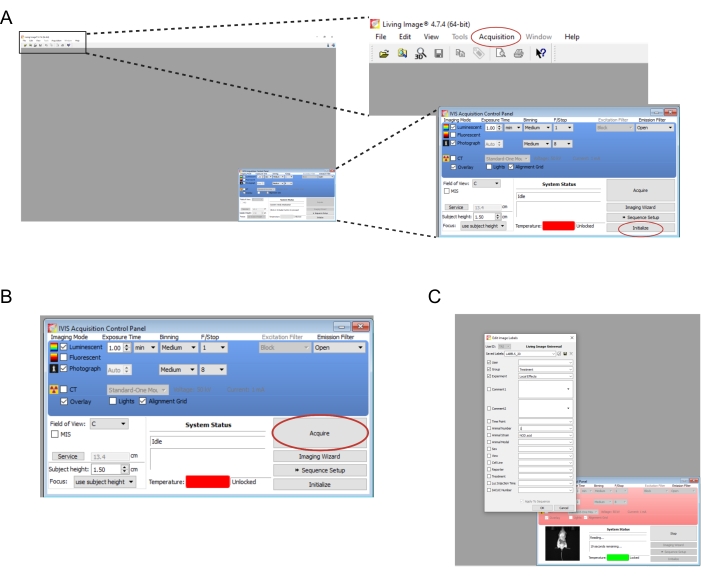
Figure 2: Screenshots of the software commands for imaging bioluminescent grafts. (A) Prior to imaging, select Initialize to prepare the instrument. The images may be auto-saved to a folder of choice by selecting Acquisition | Auto-save to… (B) Overview of the imaging parameters. Once the mouse has been positioned in the instrument, select Acquire. (C) Screenshot of the dialog box that pops up during imaging. Details such as the time point and mouse strain may be entered here. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
7. Data analysis
- Quantify the bioluminescent signal at any time after imaging. Open the software associated with the imaging instrument. Select File | Open, and select the ClickInfo.txt file associated with the mouse to be analyzed.
- In the Tool Palette, select ROI Tools (Figure 3B, Step 1). From the oval dropdown menu (Figure 3B, Step 1, red arrow), select the number of grafts that were transplanted into the mouse.
- Move the ovals so that they contain the bioluminescent signal from each graft, and select Measure ROIs (Figure 3B, Step 2).
- Record the Total Count for each graft (Figure 3B, Step 3).
- For each graft, divide the bioluminescent signal measured at every time point by the signal measured at the first time point. Report the graft survival as the proportion or percentage of residual bioluminescent signal relative to the initial bioluminescent signal.
NOTE: If the grafts expand post transplant, the ratio or percentage of graft survival will be greater than 1 or 100%, respectively. All the mice that receive transplants should be monitored for adverse health effects.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
An overview of the protocol is outlined in Figure 1. The survival of two cell lines, such as a mutant and a non-targeting control, may be compared, or the survival of one cell line may be measured in multiple groups of mice, such as drug-treated mice versus vehicle-treated controls. Figure 3A shows three 8-week-old female NOD-scid mice transplanted with a non-targeting control (left) and a mutant (right) cell line. The mice were also injected intravenously with ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
T1D is a devastating disease for which no cure currently exists. Beta cell replacement therapy offers a promising treatment for patients with this disease, but the critical barrier to this strategy is the potential for recurrent autoimmune attack against the transplanted beta cells. The genetic engineering of SC-beta cells to reduce their immune visibility or susceptibility is one potential solution to this problem. Described here is a protocol for non-invasively imaging transplanted beta cells to measure their survival ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Erica P. Cai and Dr. Yuki Ishikawa for developing the method described in this protocol (see ref. 11). Research in S.K. and P.Y.'s laboratories is supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (R01DK120445, P30DK036836), JDRF, the Harvard Stem Cell Institute, and the Beatson Foundation. T.S. was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) (T32 DK007260-45), and K.B. was supported in part by a fellowship from the Mary K. Iacocca Foundation.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.05% Trypsin, 0.53 mM EDTA | Corning | 25-052-CI | |
| 293FT | Invitrogen | R70007 | Fast-growing, highly transfectable clonal isolate derived from human embryonal kidney cells transformed with the SV40 large T antigen |
| ACK Lysing Buffer | Gibco | A10492-01 | |
| Alcohol prep pads, 70% Isopropyl alcohol | Amazon/Ever Ready First Aid | B08NWF31DX | |
| BD 5ml Syringe Luer-Lok Tip | BD | 309646 | |
| BD PrecisionGlide Needle 26G x 5/8 (0.45 mm x 16 mm) Sub-Q | BD | 305115 | |
| BD 1 mL TB Syringe Slip Tip | BD | 309659 | |
| Blasticidin S HCl | Corning | 30-100-RB | |
| Cell strainer premium SureStrain, 70 µm, sterile | Southern Labware | C4070 | Or use similar sterile strainer with 40-70um pore size |
| CellDrop automated cell counter | Denovix | CellDrop BF-PAYG | Or use similar cell counter device |
| Corning 100 mL Penicillin-Streptomycin Solution, 100x | Corning | 30-002-CI | |
| Disposable Aspirating Pipets, Polystyrene, Sterile, Capacity=2 mL | VWR | 414004-265 | Or use similar aspirating pipette |
| D-Luciferin, Potassium Salt , Molecular Biology Grade, Powder, >99% | Goldbio | LUCK-100 | |
| DMEM, high glucose, pyruvate, no glutamine | Gibco | 10313039 | |
| Falcon BD tubes, 50 mL | Fisher Scientific | 14-959-49A | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | Gibco | 10437-028 | |
| Forceps premium for tissues, 1 x 2 teeth 5 in, German Steel | Fisher Scientific | 13-820-074 | |
| Glucose urine test strip | California Pet Pharmacy | u-tsg100 | Or use similar test strip for glucose measurments in urine/blood |
| GlutaMAX–1 (100x) | Gibco | 35050-061 | |
| Infrared heating lamp | Cole Parmer | 03057-00 | Or use similar infrared lamp |
| Insulin syringe 0.5 mL, U-100 29 G 0.5 in | Becton Dickinson | 309306 | |
| Isoflurane, USP | Piramal Critical Care | 6679401725 | |
| IVIS Spectrum in vivo imaging system | Perkin Elmer | 124262 | Instrument for non-invasively collecting bioluminescent images of transplanted cells |
| Living Image Analysis Software | Perkin Elmer | 128113 | Software for collecting and quantifying bioluminescent signal |
| Microcentrifuge tubes seal-rite, 1.5 mL | USA Scientific | 1615-5510 | Or use similar sterile microcentrifuge tubes |
| NIT-1 | ATCC | CRL-2055 | Pancreatic beta-celll line derived from NOD/Lt mice |
| NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid/J | The Jackson Laboratory | 001303 | Mice homozygous for the severe combined immune deficiency spontaneous mutation Prkdcscid, commonly referred to as scid, are characterized by an absence of functional T cells and B cells, lymphopenia, hypogammaglobulinemia, and a normal hematopoietic microenvironment. |
| NOD/ShiLtJ | The Jackson Laboratory | 001976 | The NOD/ShiLtJ strain of mice (commonly called NOD) is a polygenic model for autoimmune type 1 diabetes |
| PBS, pH 7.4 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 10010031 | No calcium, no magnesium, no phenol red |
| pCMV-VSV-G | Addgene | 8454 | |
| pLenti-luciferase-blast | Made in-house | Plasmid available upon request | See Supplemental File 1 |
| pMD2.G | Addgene | 12259 | |
| pMDLg/pRRE | Addgene | 12251 | |
| Polyethylenimine, Linear, MW 25,000, Transfection Grade (PEI 25K) | Fisher Scientific | NC1014320 | |
| pRSV-Rev | Addgene | 12253 | |
| Restrainer for rodents, broome-style round 1 in | Fisher Scientific | 01-288-32A | |
| Scissors, sharp-pointed | Fisher Scientific | 08-940 | Or use other scissors made of surgical-grade stainless steel |
| Tissue-culture treated culture dishes | Millipore Sigma | CLS430167-20EA | Or use other sterile cell culture-treated Petri dishes |
| Tweezers/Forceps, fine precision medium tipped | Fisher Scientific | 12-000-157 |
References
- Katsarou, A., et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 3, 17016(2017).
- Shapiro, A. M., Pokrywczynska, M., Ricordi, C. Clinical pancreatic islet transplantation. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 13 (5), 268-277 (2017).
- Pagliuca, F. W., et al. Generation of functional human pancreatic beta cells in vitro. Cell. 159 (2), 428-439 (2014).
- Russ, H. A., et al. Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro. EMBO Journal. 34 (13), 1759-1772 (2015).
- Rezania, A., et al. Reversal of diabetes with insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells. Nature Biotechnology. 32 (11), 1121-1133 (2014).
- Vertex Announces Positive Day 90 Data for the First Patient in the Phase 1_2 Clinical Trial Dosed With VX-880, a Novel Investigational Stem Cell-Derived Therapy for the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Businesswire. , Available from: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20211018005226/en/Vertex-Announces-Positive-Day-90-Data-for-the-First-Patient-in-the-Phase-12-Clinical-Trial-Dosed-With-VX-880-a-Novel-Investigational-Stem-Cell-Derived-Therapy-for-the-Treatment-of-Type-1-Diabetes (2021).
- Gamble, A., Pepper, A. R., Bruni, A., Shapiro, A. M. J. The journey of islet cell transplantation and future development. Islets. 10 (2), 80-94 (2018).
- Pearson, J. A., Wong, F. S., Wen, L. The importance of the Non Obese Diabetic (NOD) mouse model in autoimmune diabetes. Journal of Autoimmunity. 66, 76-88 (2016).
- Hamaguchi, K., Gaskins, R. H., Leiter, E. H. NIT-1, a pancreatic β-cell line established from a transgenic NOD/Lt mouse. Diabetes. 40 (7), 842-849 (1991).
- Christianson, S. W., Shultz, L. D., Leiter, E. D. Adoptive transfer of diabetes into immunodeficient NOD-scid/scid mice: Relative contribution of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells from diabetogenic versus prediabetic NOD.NON-Thy1a donors. Diabetes. 42 (1), 44-55 (1993).
- Cai, E. P., et al. Genome-scale in vivo CRISPR screen identifies RNLS as a target for beta cell protection in type 1 diabetes. Nature Metabolism. 2 (9), 934-945 (2020).
- Parent, A. V., et al. Selective deletion of human leukocyte antigens protects stem cell-derived islets from immune rejection. Cell Reports. 36 (7), 109538(2021).
- Brehm, M. A., et al. Lack of acute xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease, but retention of T-cell function following engraftment of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in NSG mice deficient in MHC class I and II expression. FASEB Journal. 33 (3), 3137-3151 (2019).
- Abdulreda, M. H., et al. In vivo imaging of type 1 diabetes immunopathology using eye-transplanted islets in NOD mice. Diabetologia. 62 (7), 1237-1250 (2019).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved