A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Isolation and Culture of Primary Synovial Macrophages and Fibroblasts from Murine Arthritis Tissue
In This Article
Summary
The present study provides a modified protocol to isolate synovial macrophages and fibroblasts from murine inflammatory arthritis tissue.
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that leads to chronic inflammation of joints. Synovial macrophages and synovial fibroblasts have central roles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. It is important to understand the functions of both cell populations to reveal the mechanisms underlying pathological progression and remission in inflammatory arthritis. In general, in vitro experimental conditions should mimic the in vivo environment as much as possible. Primary tissue-derived cells have been used in experiments characterizing synovial fibroblasts in arthritis. In contrast, in experiments investigating the biological functions of macrophages in inflammatory arthritis, cell lines, bone marrow-derived macrophages, and blood monocyte-derived macrophages have been used. However, it is unclear whether such macrophages actually reflect the functions of tissue-resident macrophages. To obtain resident macrophages, previous protocols were modified to isolate and expand both primary macrophages and fibroblasts from synovial tissue in an inflammatory arthritis mouse model. These primary synovial cells may be useful for in vitro analysis of inflammatory arthritis.
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized by hyperplasia of the synovium, leading to joint destruction1,2. Tissue-resident macrophages and fibroblasts are present in healthy synovium to maintain joint homeostasis. In RA patients, synovial fibroblasts (SFs) proliferate, and immune cells, including monocytes, infiltrate into the synovium and joint fluid, processes associated with inflammation1,3,4. Synovial macrophages (SMs), which include resident macrophages and peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages, and SFs are aberrantly activated and have important roles in RA pathogenesis. Recent studies have suggested that cell-cell interactions between SMs and SFs contributes to both the exacerbation and remission of RA5,6.
To understand RA pathogenesis, several rodent models of inflammatory arthritis have been used, including K/BxN serum transfer arthritis, collagen-induced arthritis, and collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Cell-based assays are generally required to clarify molecular functions in arthritis. Therefore, primary cells from animal models of arthritis have been isolated. The method to isolate SFs from murine arthritis tissue is well established, and these cells have contributed to the elucidation of molecular mechanisms in arthritis pathogenesis7,8. On the other hand, bone marrow-derived macrophages, blood monocyte-derived macrophages, and macrophage cell lines have often been used as macrophage resources for arthritis studies9,10. Since macrophages can acquire functions associated with their microenvironment, general sources of macrophages may lack responses specific to arthritis tissue. In addition, it is difficult to obtain enough synovial cells by sorting, as murine synovium is a very small tissue even in arthritis models. The lack of usage of synovial macrophages for in vitro studies has been a limitation in arthritis studies. The establishment of a protocol to isolate and expand synovial macrophages would be an advantage for the elucidation of pathological mechanisms in RA.
In the previous method to isolate SFs, SMs were discarded7. Besides that, a method to isolate and expand resident macrophages from some organs was reported11. Therefore, existing protocols were modified in combination. The modification aims to achieve the primary culture of both SMs and SFs with high purity. The overall goal of this method is to isolate and expand both SMs and SFs from murine arthritis tissue.
Protocol
Experiments involving animals were approved by the Animal Experiment Committee of Ehime University and were performed in accordance with Ehime University Guidelines for Animal Experiments (37A1-1*16).
1. Preparation of instruments, reagents, and culture medium
- Prepare the culture medium as follows: supplement Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic solution (anti-anti).
- Prepare the digestion medium as follows: supplement the culture medium with 1 mg/mL collagenase type IV. Adjust the collagenase concentration just before use.
- Dilute type I-C collagen to a concentration of 0.15 mg/mL with 1 mM HCl solution. Flood culture dishes (diameter of 40 or 60 mm) with the diluted collagen solution. After 6-12 h at room temperature, remove the collagen solution from the dishes and dry at room temperature. The collagen-coated dishes can be kept at room temperature for at least 1 week. Wash the pre-coated dishes with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) or medium before use.
- Prepare sterile surgical instruments, such as scissors, tweezers with serrated tips, and fine-point tweezers. Soak in 70% ethanol before use.
2. Preparation of synovitis tissue in mice ( Figure 1A)
- Prepare a mouse with inflammatory arthritis in the hind paws.
NOTE: Female C57BL/6 mice (18-20 g), 7-8 weeks postnatal, with collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) or K/BxN serum transfer arthritis (STA) were used for this protocol8. Isolating SMs from non-swollen (i.e., healthy) tissue might be difficult, as the number of cells is insufficient. - Anesthetize the mice by an intraperitoneal injection of 80 mg/kg ketamine and 16 mg/kg xylazine. Clean the mice with 70% ethanol.
- Cut open the pectoral region with scissors to expose the heart. Cut the right auricle of the heart with scissors, and then stick a 23 G butterfly needle into the left ventricle via apex of the heart, followed by a reflux of 15-20 mL of sterile PBS using a syringe to manually remove peripheral blood (approximately 1 mL/2 s).
- Decorticate the hind paws by cutting the skin using scissors and pulling skin using tweezers with serrated tips.
NOTE: After this step, the usage of tweezers is recommended for the handling of samples. Don't touch decorticated tissue with fingers, to avoid the attachment of murine hair. - Dislocate the metatarsophalangeal joints by pulling, followed by cutting the ligaments of the joints using scissors to remove the toes.
- Cut the tendons of the lower leg muscles near the ankle using scissors. Grasp the tendon with tweezers and peel the muscles proximally in the lower leg to expose the tibia. Remove the fibula.
- Dislocate the knee joint by pulling, followed by cutting the ligaments of the joints using scissors to detach the tibia with the swollen hind paw. Keep the samples in ice-cold culture medium (0.3 mL/cm2) until processing to step 3.1.
3. Digestion of synovitis tissue ( Figure 1B)
- Aspirate the culture medium, avoiding the sample, and then add fresh culture medium (0.3 mL/cm2). Repeat the washing process three or four times.
NOTE: From this step, the handling of samples should be performed aseptically in a clean bench or safety cabinet. - Dislocate all the joints of the samples by pulling using fine-point tweezers in the culture medium under a stereomicroscope (at 10x-20x magnification). Fine-point tweezers are convenient in this step. Remove the tibia and as many vessels, tendons, and ligaments as possible. Be careful not to break the bones when dislocating.
- Prepare two 15 mL tubes per sample. Transfer the dislocated bones with soft tissues to the first 15 mL tube using tweezers. Add 4 mL of digestion medium per sample, obtained from both hind paws, into the tube.
- To collect residual cells and tissue fragments, transfer the medium in which the sample was contained to the second 15 mL tube. Centrifuge the medium at 500 x g for 5 min at room temperature. After removing the supernatant, resuspend the pellet with 1 mL of digestion medium and transfer the cell and tissue fragment solution to the first 15 mL tube containing almost all the tissue (total of 5 mL of digestion medium/hind paws).
- Digest the sample for 60-120 min at 37 °C with shaking in a hybridization oven.
NOTE: The optimal time to digest the samples should be decided. The time is dependent on the degree of swelling in the ankles and collagenases. In most cases, 60-120 min is sufficient. After 60 min of incubation, collect a part of the digested sample by pipetting, and observe under a microscope. If the digestion is insufficient, the incubation should continue, and the digestion checked every 30 min. - Pipet the solution well. Filter the cell solution through a cell strainer (40 µm pore size) to a 50 mL tube.
- Add 10 mL of culture medium to the 50 mL tube through the cell strainer. Centrifuge at 300 x g for 5 min at room temperature.
- After removing the supernatant, resuspend with 10 mL of culture medium. Repeat the centrifugation. After removing the supernatant, resuspend with 2 mL of culture medium.
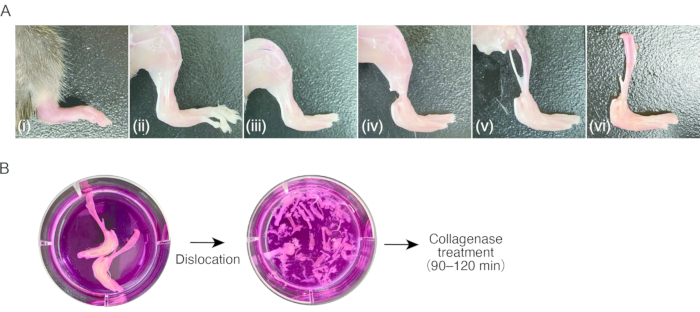
Figure 1: Procedure of sampling of murine arthritis tissue and collagenase digestion. (A) (i) Murine hind paw with inflammatory arthritis. (ii) Removal of the skin on the hind paw. (iii) Dislocation of the metatarsophalangeal joints and removal of the toes. (iv) Cutting of the tendons in the ankle. (v) Removal of the muscles in the lower legs. (vi) Dislocation of the knee joint. (B) Left; excised legs in culture medium. Right; dislocated tarsus and metatarsus in culture medium. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Isolation of synovial fibroblasts ( Figure 2A)
- Seed all cell suspensions obtained from both ankles on the collagen-coated dish.
NOTE: If using ankles with weak or moderate swelling to obtain the cells, a 40 mm diameter dish is applied. The collagen-coated dish size can be changed to a 60 mm diameter dish if both ankles have severe swelling. - Add culture medium (approximately 222 µL/cm2). Incubate for 1 h at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
- Collect non-adherent cells using a pipet (use in step 5.1). Wash the collagen-coated dish with culture medium and collect the medium. Culture the adherent cells in fresh medium (Figure 2B,i). Most of the cells that quickly adhere to the collagen-coated dish exhibit a fibroblastoid (spindle-shaped) morphology.
- Passage sub-confluent cells by treatment with 0.05% trypsin in Hanks' balanced salt solution (HBSS). In this method, the contamination of other cells is limited, even if in the initial expansion. If more purified fibroblast-like cells are required, perform repeated passaging to allow enhancement of the purity; however, the expansion of the cells' cytoplasm in adhesion is also observed (Figure 2B,ii). Since excessive passages affect the loss of naïve characteristics in the cells, use cells with fewer than 5 passages.
5. Isolation of synovial macrophages ( Figure 2A)
- Seed all non-adherent cells from step 4.4 on dishes (diameter of 40 or 60 mm) that have not been coated with collagen.
NOTE: Non-adherent cells include macrophages, other lymphocytes, and residual fibroblasts from synovitis tissue. - Culture the bulk cells for 1 day at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
- To remove non-adherent lymphocytes, aspirate the cultured medium, and then add fresh culture medium. Repeat this process two or three times (Figure 2B,iii).
- Culture the adherent bulk cells for 1-2 weeks in culture medium, with medium changes every 2 days while maintaining confluence (Figure 2B,iv).
NOTE: The number of SMs slowly increases under co-culture conditions with SFs. Thus, the co-culture period should be adjusted as needed. - Wash with PBS or HBSS two times. Treat with 0.05% trypsin in HBSS (approximately 55 µL/cm2) for 3 min at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Fibroblasts easily detach from the culture dish by trypsin treatment, and macrophages exhibit resistance to trypsin treatment. Use this property for the selection of synovial macrophages.
- Add culture medium (approximately 222 µL/cm2) gently to 0.05% trypsin in HBSS. After this step, do not pour the medium directly onto the cells.
- To remove detached cells, aspirate the cultured medium, and then add fresh culture medium gently. Repeat this process two or three times. Maintain the remaining cells on the dish in fresh culture medium until use (Figure 2B,v).
NOTE: Following trypsin treatment, adherent cells exhibit macrophage-like morphological characteristics.

Figure 2: Separation of macrophage-rich and fibroblast-rich fractions from inflammatory arthritis tissue. (A) Schema of the procedure to separate macrophage-rich and fibroblast-rich cells from arthritis tissue. (B) Representative phase contrast images of stages of the procedure, (i) to (v) in Figure 2A. Scale bar represents 100 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
Female C57BL/6 mice at 7-8 weeks of age underwent collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Macrophage-like cells and fibroblast-like cells were independently isolated from inflammatory arthritis tissue according to the procedure described above (Figure 2A,B). Macrophage-like cells were immediately used after step 5.7. Fibroblast-like cells were initially cultured to be sub-confluent after step 4.4, and then passaged to a new culture dish followed by usage. To evaluate whether SM...
Discussion
This method developed here improves upon previous techniques for isolating both SFs from murine arthritis and resident macrophages from a number of organs7,11. The modified method can isolate both macrophages and fibroblasts from inflammatory synovium with high purity, and it is simple and reproducible. Since the method does not require complex instruments such as a cell sorter, anyone can conduct it. In addition, the present technique avoids concerns associated ...
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the staff at the Division of Medical Research Support, the Advanced Research Support Center (ADRES), and the members of the Division of Integrative Pathophysiology, Proteo-Science Center (PROS), Ehime University, for their technical assistance and helpful support. This study was supported in part by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI grants JP17K17929, JP19K16015, JP21K05974 (to NS) and JP23689066, JP15H04961, JP15K15552, JP17K19728, JP19H03786 (to YI); grants from the Osaka Medical Research Foundation for Intractable Diseases, The Nakatomi Foundation, The Japanese Society for Bone and Mineral Research (JSBMR) Rising Stars Grant, The Sumitomo Foundation, SENSHIN Medical Research Foundation, The Mochida Memorial Foundation (to NS); and a Takeda Science Foundation Medical Research grant, UCB Japan (UCBJ) project grant, and the JSBMR Frontier Scientist grant 2019 (to YI).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 5.0 g/L Trypsin/5.3 mmol/L EDTA solution | nacalai tesque | 35556-44 | Diluted with HBSS |
| Antibiotic–antimycotic (anti/anti) | Gibco | 15240-062 | |
| Butterfly needle | TERUMO | SV-23DLK | 23G |
| Cell strainer | Falcon | 352340 | 40 µm pore, Nylon |
| Cellmatrix Type I-C | Nitta gelatin | 637-00773 | Type I-C collagen |
| Centriguge tube 15 | TPP | 91014 | 15 mL tube |
| Centriguge tube 50 | TPP | 91050 | 50 mL tube |
| Collagenase from C. Histolyticum | Sigma | C5138 | Type IV collagenase |
| Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium GlutaMax (DMEM) | Gibco | 10569-010 | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | SIGAM | 173012 | Heat inactivation was performed |
| Hanks' balanced salt solution (HBSS) | Wako | 085-09355 | |
| Scissors | Bio Research Center | PRI28-1525A | |
| Tissue culture dish 40 | TPP | 93040 | For cell culture |
| Tissue culture dish 60 | TPP | 92006 | For cell culture |
| Tweezers | KFI | 1-9749-31 | Fine-point |
| Tweezers | Bio Research Center | PRI28-1522 | Serrated tip |
| ZEISS Stemi 305 | ZEISS | STEMI305-EDU | Stereomicroscope |
References
- Smolen, J. S., Aletaha, D., McInnes, I. B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 388 (10055), 2023-2038 (2016).
- McInnes, I. B., Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. The New England Journal of Medicine. 365 (23), 2205-2219 (2011).
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M., Alivernini, S. Synovial tissue macrophages: friend or foe. RMD Open. 3 (2), (2017).
- Hannemann, N., Apparailly, F., Courties, G. Synovial macrophages: from ordinary eaters to extraordinary multitaskers. Trends in Immunology. 42 (5), 368-371 (2021).
- Alivernini, S., et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Medicine. 26 (8), 1295-1306 (2020).
- Saeki, N., Imai, Y. Reprogramming of synovial macrophage metabolism by synovial fibroblasts under inflammatory conditions. Cell Communication and Signaling. 18 (1), 188 (2020).
- Armaka, M., Gkretsi, V., Kontoyiannis, D., Kollias, G. A standardized protocol for the isolation and culture of normal and arthritogenic murine synovial fibroblasts. Protocol Exchange. , (2009).
- Saeki, N., et al. Epigenetic regulator UHRF1 orchestrates proinflammatory gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis in a suppressive manner. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 132 (11), (2022).
- Midwood, K., et al. Tenascin-C is an endogenous activator of Toll-like receptor 4 that is essential for maintaining inflammation in arthritic joint disease. Nature Medicine. 15 (7), 774-780 (2009).
- You, D. G., et al. Metabolically engineered stem cell-derived exosomes to regulate macrophage heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis. Science Advances. 7 (23), 0083 (2021).
- Ogawa, K., Tsurutani, M., Hashimoto, A., Soeda, M. Simple propagation method for resident macrophages by co-culture and subculture, and their isolation from various organs. BMC Immunology. 20 (1), 34 (2019).
- Andrä, I., et al. An evaluation of T-cell functionality after flow cytometry sorting revealed p38 MAPK activation. Cytometry Part A. 97 (2), 171-183 (2020).
- Ryan, K., Rose, R. E., Jones, D. R., Lopez, P. A. Sheath fluid impacts the depletion of cellular metabolites in cells afflicted by sorting induced cellular stress (SICS). Cytometry Part A. 99 (9), 921-929 (2021).
- Llorente, I., García-Castañeda, N., Valero, C., González-Álvaro, I., Castañeda, S. Osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis: dangerous liaisons. Frontiers in Medicine. 7, 601618 (2020).
- Croft, A. P., et al. Distinct fibroblast subsets drive inflammation and damage in arthritis. Nature. 570 (7760), 246-251 (2019).
- Wei, K., et al. Notch signalling drives synovial fibroblast identity and arthritis pathology. Nature. 582 (7811), 259-264 (2020).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved