A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Intact Short, Intermediate, and Long Skeletal Muscle Fibers Obtained by Enzymatic Dissociation of Six Hindlimb Muscles of Mice: Beyond Flexor Digitorum Brevis
In This Article
Summary
We describe a protocol to obtain enzymatically dissociated fibers of different lengths and types from six muscles of adult mice: three of them already described (flexor digitorum brevis, extensor digitorum longus, soleus) and three of them successfully dissociated for the first time (extensor hallucis longus, peroneus longus, peroneus digiti quarti).
Abstract
Skeletal muscle fibers obtained by enzymatic dissociation of mouse muscles are a useful model for physiological experiments. However, most papers deal with the short fibers of the flexor digitorum brevis (FDB), which restrains the scope of results dealing with fiber types, limits the amount of biological material available, and impedes a clear connection between cellular physiological phenomena and previous biochemical and dynamical knowledge obtained in other muscles.
This paper describes how to obtain intact fibers from six muscles with different fiber type profiles and lengths. Using C57BL/6 adult mice, we show the muscle dissection and fiber isolation protocol and demonstrate the suitability of the fibers for Ca2+ transient studies and their morphometric characterization. The fiber type composition of the muscles is also presented. When dissociated, all muscles rendered intact, living fibers that contract briskly for more than 24 h. FDB gave short (<1 mm), peroneus digiti quarti (PDQA) and peroneus longus (PL) gave intermediate (1-3 mm), while extensor digitorum longus (EDL), extensor hallucis longus (EHL), and soleus muscles released long (3-6 mm) fibers.
When recorded with the fast dye Mag-Fluo-4, Ca2+ transients of PDQA, PL, and EHL fibers showed the fast, narrow kinetics reminiscent of the morphology type II (MT-II), known to correspond to type IIX and IIB fibers. This is consistent with the fact that these muscles have over 90% of type II fibers compared with FDB (~80%) and soleus (~65%). Moving beyond FDB, we demonstrate for the first time the dissociation of several muscles, which render fibers spanning a range of lengths between 1 and 6 mm. These fibers are viable and give fast Ca2+ transients, indicating that the MT-II can be generalized to IIX and IIB fast fibers, regardless of their muscle source. These results increase the availability of models for mature skeletal muscle studies.
Introduction
The mature skeletal muscle of mammals is a multifunctional tissue. It heavily regulates metabolism, is the main source of heat production, and its dynamical properties confer upon it a key role in respiration, movement of body segments, or displacement from one point to another1,2,3. Skeletal muscle is also relevant for the pathophysiology of many illnesses, including inherited and chronic conditions, such as myopathies, dystrophies, or sarcopenia, as well as many non-muscle chronic conditions, such as cardiometabolic diseases3,4,5,6,7,8.
The ex vivo study of the structural and functional properties of mature skeletal muscle in the context of health and disease has been possible mainly through two experimental models: whole muscle and isolated fibers. In the 20th century, researchers exploited the properties of the whole, intact extensor digitorum longus (EDL), soleus, tibialis anterior, and gastrocnemius muscles of different small species as pivotal models to learn about motor units, fiber types, and dynamic properties such as force and kinetics of contraction and relaxation9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16. However, the advent of more refined cell biology studies moved the area toward the study of single muscle fibers. Pioneering work then enabled the isolation of intact flexor digitorum brevis (FDB) fibers of rats by enzymatic dissociation for subsequent characterization17,18,19. Although FDB fibers can also be obtained by manual dissection20, the ease and high throughput of enzymatic dissociation of murine muscles, in addition to their suitability for a variety of experimental approaches, have made the latter model widely used during the last two decades.
The short FDB fibers are suitable for electrophysiological and other biophysical studies, biochemical, metabolic, and pharmacological analyses, electron and fluorescence microscopy experiments, transfection for cell biology approaches, or as a source of stem cells in myogenesis studies5,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32. However, using only FDB fibers in muscle experiments narrows the scope of research dealing with fiber types and limits the amount of biological material available for some methodological techniques or for gaining more information from one animal. These limitations hinder a clear correlation of cellular physiological phenomena with previous biochemical and dynamical studies performed in different whole, intact, muscles (e.g., EDL, soleus, peronei).
Overcoming these limitations, some groups succeeded in dissociating the longer EDL and soleus muscles24,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40, opening the door to further extend the method to other relevant muscles. However, the use of EDL and soleus fibers is still scarce, likely due to the lack of methodological details for getting them as intact fibers. Here, we describe in detail how to isolate fibers of different lengths and types from six muscles: three of them already described (FDB, EDL, and soleus) and three of them successfully dissociated for the first time (extensor hallucis longus [EHL], peroneus longus [PL], and peroneus digiti quarti [PDQA]). The results of the present work confirm that the model of enzymatically dissociated fibers is apt for a wide range of studies and future correlations with previously published data, thus increasing the availability of models for mature skeletal muscle studies.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
All procedures were approved by the Committee for Ethics in Experiments with animals of the University of Antioquia (UdeA) (minutes 104 of June 21st, 2016, and 005 of April 15th, 2021), according to Law 84 of 1989 and Resolution 8430 of 1993 issued by the Colombian Government and were performed and reported in compliance with the Animal Research: Reporting In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines41. All results presented here come from healthy, 7-13 weeks old, 20-26 g, C57BL/6 male mice. Figure 1 shows the general design of this study and the order of the procedures. All reagents, materials, and equipment details are listed in the Table of Materials.
1. Animals
- House a maximum of six mice per acrylic, transparent, rectangular cage, with wood-derived bedding, under conditions of controlled temperature (21 ± 2 °C) and light:darkness (12:12 h) cycles.
- Give the animals free access to food and tap water in specific pathogen-free animal facilities with no environmental enrichment.
2. Dissection
- Solutions, materials, and reagents
- Prepare and filter (0.22 µm) the working solutions with the following composition (all concentrations in mM):
- Tyrode: 5.4 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 140 NaCl, 0.33 NaH2PO4, 2 CaCl2, 10 glucose, 10 HEPES, pH 7.3
- Dissociation: 2.7 KCl, 1.2 KH2PO4, 0.5 MgCl2, 138 NaCl, 0.1 Na2HPO4, 1 CaCl2, pH 7.4
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS): 137 NaCl, 8.6 Na2HPO4, 2.8 KH2PO4, pH 7.34
- Prepare two dissection chambers; stereoscope; operating scissors; fine scissors; fine forceps; and clean, transparent, non-conic, 1-1.5 cm wide, glass vials of 3-4 mL total volume with caps. Arrange a system for electrically stimulating the muscles in the dissection chambers.
- Prepare fire-polished Pasteur glass pipettes of different width tips: 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1 mm.
- Set the water bath to 37 °C. Weigh aliquots of 3 mg of collagenase type 2.
- Prepare and filter (0.22 µm) the working solutions with the following composition (all concentrations in mM):
- Procedure
- Sacrifice the mouse using methods approved by the local Ethics Committee. Cervical dislocation is recommended because it is rapid, less stressful, and avoids exposure to drugs, which may affect the muscle tissue (such as CO2 or some anesthetics). Start dissection immediately to obtain better results.
- Place the mouse on a foam surface and tape or pin the forelimbs. Cut both hindlimbs over the knees with the operating scissors, transfer each of them to a separate dissection chamber, and add cold (10-20 °C) Tyrode to cover the tissue.
NOTE: Each hindlimb will give six different muscles in the following order: FDB, soleus, EDL, EHL, PL, and PDQA. Detailed anatomical references to dissect the six muscles intact from tendon to tendon are given in Figure 2 and elsewhere42. - Pin the first hindlimb to the dissection chamber in a position in which the posterior face of the legs is visible. Remove the skin under magnification; then expose and remove the FDB (Figure 2). Store it in one labeled glass vial with 1 mL of Tyrode solution.
NOTE: Appropriate magnification and previous training are required to avoid any undesired cut in the muscle tissue. - Expose, remove, and store the soleus in a separate vial with 1 mL of Tyrode. Use fine scissors to first separate the gastrocnemius and then to remove the soleus, as indicated in Figure 2.
- Expose the anterior face of the leg, remove the skin, and identify the distal tendons of the tibialis anterior and the EDL muscles in the ankle. Remove and discard the tibialis; then cut the distal tendons of the EDL (Figure 2). Continue dissection until removing the EDL and place it in a separate glass vial with 1 mL of Tyrode.
- Remove the EHL muscle, which lies just posterior and medial to the EDL. Start dissection by identifying and following the tendon to the 1st digit, as indicated in the corresponding panel of Figure 2. Keep the muscle in a separate glass vial with 1 mL of Tyrode.
- Identify and follow the most external tendon of the peronei to cut it and remove the PL muscle (Figure 2). Place the muscle in a separate glass vial with 1 mL of Tyrode.
- Identify and follow the tendon to the 4th digit; cut it and remove the PDQA muscle (Figure 2). Place it in a separate glass vial with 1 mL of Tyrode.
- Repeat the procedure with the second hindlimb.
- Gather both muscles of the same type in one labeled glass vial or a small Petri dish with Tyrode solution.
NOTE: If more than two pairs of muscles are planned to be dissected during a working session, recruit two researchers for the dissection procedure.
3. Muscle fiber isolation protocol
- Renew the Tyrode solution in the dissection chambers to remove debris and mouse fur. Pour the FDB muscles into one dissection chamber, verify their integrity, and transfer them to a new glass vial with 1 mL of dissociation solution. Repeat this procedure with the EHL, PL, and PDQA muscles.
NOTE: If a muscle looks hypercontracted, cut, or is unresponsive to the electrical stimulation, do not continue to the next protocol step. Instead, optimize the dissection protocol by verifying the quality of the solutions (pH, contamination, osmolarity) and gaining more dissection skills (Figure 1C and Supplemental Video S1). - Perform longitudinal or diagonal cuts to the soleus and EDL muscles, following the orientation of the fibers (Figure 2). For the soleus, follow the central tendon, cutting ~80% of its length. For EDL, just follow one or two tendons and cut about the same length as for soleus. Put each pair of muscles in glass vials with 1 mL of dissociation solution.
NOTE: This procedure makes the EDL and soleus smaller and allows for the collagenase to better enter the tissue. Sufficient magnification (40-50x), as well as fine scissors and forceps, are mandatory. Always check sample integrity by visual inspection and electrical stimulation before continuing to the next step of the dissociation protocol. - Add 3 mg of collagenase type 2 (with an activity of 250-300 U/mg) to each vial containing 1 mL of dissociation solution and a pair of muscles. Standardize the exact amount of collagenase by considering the activity of the enzyme batch used.
- Incubate the pairs of muscles in the water bath for 65-90 min at 36.8-37 °C, with gentle shaking.
NOTE: Be rigorous with the temperature control. Standardize the procedure so that the muscles do not remain in collagenase for more than 100 min to avoid damage. - Check the vials under stereoscope magnification every 5 min after the 65th min of incubation. When the muscles look slightly rippled, ragged, and loose, gently shake the vial and verify if some fibers start detaching readily. If this is the case, wash the muscles with Tyrode at room temperature to inactivate and remove the collagenase.
NOTE: Washing must be done carefully, without touching the muscles with the pipettes. Start by adding 0.8 mL of Tyrode and then remove 0.8 mL of the solution. Repeat this procedure 4-5x and verify that the solution becomes fully transparent. - Separate more fibers from the bulk of the muscles with very gentle trituration in Tyrode with the help of the set of fire-polished Pasteur pipettes. Start by agitating the solution around the muscle with the widest pipette (5 mm tip) and then gently pull the muscles up into and out of the pipette 3-4x. When the muscle starts releasing fibers and becomes thinner, repeat the procedure with the next pipette (4 mm tip).
NOTE: Fibers rendered via this procedure remain excitable and contract briskly for more than 24 h, as exemplified using PL, EDL, EHL, and soleus fibers in Supplemental Video S2, Supplemental Video S3, Supplemental Video S4, and Supplemental Video S5.
4. Experimental procedures
NOTE: Isolated fibers were used for sarcoplasmic Ca2+ concentration estimations, morphometric measurements, and myosin heavy chain (MHC) expression studies.
- Measurement of the sarcoplasmic Ca2+ concentration during a twitch
- Mount a clean, glass slide on the experimental bath chamber. Coat the slide with 2-3 µL of laminin and allow it to dry for 30 s before pouring ~400 µL of the fiber suspension onto the slide. Allow the fibers to adhere to the laminin for 10-15 min at room temperature.
- Mount the experimental chamber onto the stage of an inverted microscope equipped for epifluorescence (Figure 3A).
- Evoke single twitches to verify the viability of the fibers by applying rectangular current pulses (0.8-1.2 ms) through the two platinum electrodes placed along either side of the experimental chamber. Even when attached to laminin, the contraction of the fibers is still visible mainly at the extremes.
- Load the fibers with 3.5-4.5 µM of the fast Ca2+ dye Mag-Fluo-4, AM for 4-5 min in Tyrode solution. After this time, gently wash with Tyrode to remove the extracellular dye. Allow the intracellular dye to be de-esterified for ~15-20 min under dark conditions. Always keep the temperature below 22 °C to avoid the dye compartmentalization.
NOTE: Prepare a stock of Mag-Fluo-4, AM in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) only, so that the final concentration of DMSO in the loading Tyrode solution is less than 0.5%. - Illuminate the fiber with a white light-emitting diode (LED) and a filter set with the following wavelengths for excitation/dichroic/emission: 450-490/510/515 nm (Figure 3A).
NOTE: Alternative sources of excitation include mercury and xenon fluorescence lamps. Use the lowest possible intensity and size of the excitation spot to avoid photobleaching of the dye and damage to the cell. - Evoke the fiber´s Ca2+ response (sarcoplasmic Ca2+ transients) by applying rectangular current pulses (0.8-1.2 ms) through the two platinum electrodes placed along either side of the experimental chamber at 20-22 °C.
- Collect and save the light signals with an oil immersion 40x long-distance objective suitable for fluorescence and a photomultiplier tube (PMT) connected to a digitizer (Figure 3A and Supplemental Video S6). Ensure a scale in the acquisition software of 0-200 arbitrary units (AU) and set the resting fluorescence (Frest) of the experiment to 10 AU on that scale by modulating the size of the excitation spot and the gain of the PMT. Once the procedure is standardized, keep the gain unmodified from one experiment to the other and set the scale only through minor adjustments in the spot size.
NOTE: If movement artifacts arise, use 20-30 µM N-benzyl-p-toluene sulphonamide (BTS) in the Tyrode solution. - Analyze and calibrate the signals as follows:
- Lowpass filter the whole trace at 1 kHz.
- Calculate the Frest in 1 s of the trace, adjust the Frest to 0, and measure the peak sarcoplasmic Ca2+ transients ' amplitude (Fpeak). Present the amplitude as in equation (1):
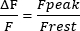 (1)
(1) - Calculate the peak Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+], µM) using equation (2)26 and the following parameters: in situ dissociation constant (Kd) = 1.65 × 105 µM2, maximum fluorescence (Fmax) of 150.9 AU, minimum fluorescence (Fmin) of 0.14 AU, Mag-Fluo-4 concentration [D]T of 229.1 µM26. Fpeak was already obtained in step 4.1.8.2.
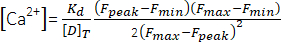 (2)
(2) - Measure the rise time from 10% to 90% of the amplitude (RT, ms), the duration at half maximum (HW, ms), and the decay time from 90% to 10% of the amplitude (DT, ms). Then, estimate the decay kinetics according to a fit with the biexponential function (equation 3):
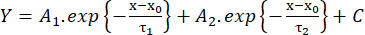 (3)
(3) - Save the values of the time constants of decay τ1 and τ2 (ms) and amplitudes A1 and A226.
- Morphometric measurements
- Mount a clean, glass slide on the experimental bath chamber. Coat the slide with 2-3 µL of laminin and allow it to dry for 30 s before pouring ~400 µL of the fiber suspension onto the slide. Allow the fibers to adhere to the laminin for 10-15 min at room temperature.
- Evoke single twitches to verify the viability of the fibers by applying rectangular current pulses (0.8-1.2 ms) through the two platinum electrodes placed along either side of the experimental chamber. Even when attached to laminin, the contraction of the fibers is still visible mainly at the extremes.
- Acquire images of the alive fibers using 10x and 20x objectives and a camera of at least 5 megapixels mounted on an inverted fluorescence microscope. Store the images in .TIFF format for offline analyses.
NOTE: A set of ~2-6 images may be needed to completely capture a long fiber. - Image a microscope micrometer calibration ruler under the same magnification. Store the images in .TIFF format for offline analyses.
- Measure the lengths and diameters of the fibers using the calibration tool of free software for image analyses as follows:
- Establish a relation between pixels and the known distance (µm) in the images with the help of the microscope micrometer calibration ruler by using the Analyze/Set scale tool as shown in Supplemental Figure S1.
- Measure lengths once from one tip to the other of the fiber and diameters in 2-6 different places along the fiber (1-2 measurements per image, depending on its length), as in Supplemental Figure S1.
- Report the value of length (µm or mm) and the average of all diameters (µm) measured per fiber.
- Myosin heavy chain expression studies
NOTE: For details about the determination of MHC by immunofluorescence43 and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)33,44,45,46 in whole muscles, please see Supplemental File 1. The protocol for fiber typing by immunofluorescence determination of MHC in the suspension of FDB-isolated fibers is as follows:- Coat each of five clean, glass slides with 2-3 µL of laminin and allow it to dry for 30 s before pouring ~300 µL of the fiber suspension onto each slide. Allow the fibers to adhere to the laminin for 4 h at room temperature.
- Fix the preparations with freezer-cooled acetone for 30 min at room temperature.
- Wash gently 3x with PBS.
- Permeabilize the cell membranes with PBS supplemented with 0.7% Triton X-100 for 15 min at room temperature.
- Wash gently 3x with PBS supplemented with 0.2% bovine serum albumin (BSA) and 0.04% Triton X-100, and subsequently block with PBS with 2% BSA, 2% goat serum, and 0.4% Triton X-100 for 30 min at room temperature.
- Wash gently 3x with PBS supplemented with 0.2% BSA and 0.04% Triton X-100 and incubate with the primary antibodies as follows:
- Dilute each anti-MHC primary antibody in a separate vial in PBS with 1% BSA and 0.04% Triton X-100: anti-I (1:1,500), anti-II (1:600), anti-IIA (use entire conditioned media from the hybridoma), and anti-IIB (1:500).
- Incubate each slide with one antibody and the remaining slide with PBS as a control for 12-16 h at 4 °C.
NOTE: In this protocol, fibers type IIX remained unlabeled in all samples.
- Wash gently 3x with PBS and incubate all slides with the secondary antibody (1:800) coupled to a fluorescent green molecule for 1-2 h at room temperature.
- Stain nuclei with 1 µg/mL Hoechst for 15 min.
- Wash gently 3x with PBS, carefully add 20-40 µL of mounting medium, and place a coverslip.
NOTE: Gentle solution exchanges and washing ensure that dozens of fibers remain attached to the slide, making the experiment statistically sound. - Visualize each slide using a 10x objective suitable for fluorescence and a filter set with the following wavelengths for excitation/dichroic/emission: 450-490/510/515 nm and count all positive and negative fibers. Alternatively, acquire fluorescence images using the same technical conditions and a camera of at least 5 megapixels mounted on an inverted fluorescence microscope and store them in .TIFF format for offline analyses.
- Record the positive and negative fibers of each slide in a database and calculate the percentages of positive I, IIA, IIB, and total II fibers based on the total number of fibers present in the corresponding slide. Calculate the percentage of IIX fibers by subtracting the sum of IIA+IIB from the percentage of total II fibers. Estimate the percentage of hybrid I/IIA fibers by subtracting the sum of I+II from a value of 100%. Finally, subtract the percentage of hybrid cells from the total of I and II to have the pure type I and II fibers.
NOTE: In MHC composition studies, fiber types are designated by a capital letter while isoforms are designated by a lowercase letter46.
- Hematoxylin and eosin staining
- Coat a clean, glass slide with 2-3 µL of laminin and allow it to dry for 30 s before pouring ~300 µL of the fiber suspension onto the slide. Allow the fibers to adhere to the laminin for 4 h at room temperature.
- Fix the preparation with Carnoy´s solution (60% absolute ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) for 5 min at room temperature.
- Incubate with hematoxylin for 90 s.
- Wash gently 3x with tap water.
- Incubate with 1% eosin Y prepared in 70% ethanol for 30 s.
- Wash gently 3x with tap water.
- Immerse 3x into absolute ethanol.
- Incubate in xylol for 60 s.
- Add 20-40 µL of mounting medium and visualize with a conventional microscope. Acquire images at the desired magnification using a color camera of at least 5 megapixels.
5. Statistical analyses and graphing
NOTE: The experimental unit is a muscle fiber.
- Express results as mean ± standard deviation and calculate confidence intervals 95% (CI95%) for some analyses.
- To compare length, diameter, and Ca2+ transients´ kinetics among groups, perform analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post-hoc tests with the correction of Bonferroni.
- Assess normality and variance equality using the Shapiro-Wilk and Levene's tests, respectively.
- Consider the differences significant when p < 0.05.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Sarcoplasmic Ca2+ concentration during a twitch
To demonstrate the feasibility of physiological experiments in the set of dissociated fibers and to extend our previous findings on excitation-contraction coupling (ECC) and fiber types, Ca2+ transients were acquired in fibers from all muscles. First, FDB (n = 5) and EDL (n = 7) showed Ca2+ kinetics known as morphology type II (MT-II). These are fast, spiky signals, whose RT lasts ~1 ms; its decay phase can be fitted wit...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
To complement the models available for studying mature skeletal muscle biology, here we demonstrate the successful enzymatic dissociation of a range of mouse muscles with short, intermediate, and long fibers. These fibers allow for the demonstration of the generalizability of the MT-II kinetics of the Ca2+ transients in skeletal muscle. Further, the fiber types in the intact, whole muscles were classified. Given that the FDB is the most used muscle for physiological experiments, the types of fibers present in ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Professor Robinson Ramírez from UdeA for help with animals and some photos and to Carolina Palacios for technical support. Johan Pineda from Kaika helped us to set up the color and fluorescence cameras. Shyuan Ngo, from the University of Queensland, kindly proofread the manuscript. This study was funded by the CODI-UdeA (2020-34909 from February 22nd, 2021, and 2021-40170 from March 31st, 2022, SIU), and Planning Office-UdeA (E01708-K and ES03180101), Medellín, Colombia, to JCC. Funders did not participate in data collection and analysis, manuscript writing or submission.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Reagents | |||
| Absolute ethanol | Sigma Aldrich | 32221 | |
| Acetone | Merck | 179124 | |
| Acrylamide | Gibco BRL | 15512-015 | |
| Ammonium persulfate | Panreac | 141138.1610 | |
| Anti myosin I antibody | Sigma Aldrich | M4276 | Primary antibody |
| Anti myosin II antibody | Sigma Aldrich | M8421 | Primary antibody |
| Anti myosin IIA antibody | American Type Culture Collection | SC-71 | Primary antibody. Derived from HB-277 hybridoma |
| Anti myosin IIB antibody | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | BF-F3-c | Primary antibody |
| Bis-acrylamide | AMRESCO | 0172 | |
| Bovine serum albumin | Thermo Scientific | B14 | |
| Bradford reagent | Merck | 1.10306.0500 | |
| Bromophenol blue | Carlo Erba | 428658 | |
| Calcium carbonate | Merck | 102066 | |
| Calcium dichloride (CaCl2) | Merck | 2389 | |
| Chloroform | Sigma Aldrich | 319988 | |
| Collagenase type 2 | Worthington | CLS-2/LS004176 | |
| Consul-Mount | Thermo Scientific | 9990440 | |
| Coomassie Brilliant blue R 250 | Merck | 112553 | |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | Sigma Aldrich | D2650 | |
| Dithiothreitol (DTT) | AMRESCO | 0281 | |
| Edetic acid (EDTA | AMRESCO | 0322 | |
| Eosin Y | Sigma Aldrich | E4009 | |
| Glycerol | Panreac | 1423291211 | |
| Glycine | Panreac | 151340.1067 | |
| Goat serum | Sigma Aldrich | G9023 | |
| Hematoxylin | Thermo Scientific | 6765015 | |
| HEPES | AMRESCO | 0511 | |
| Hoechst 33258 | Sigma Aldrich | 861405 | |
| Imidazole | AMRESCO | M136 | |
| Isopentane | Sigma Aldrich | M32631 | |
| Laminin | Sigma Aldrich | L2020 | |
| Mag-Fluo-4, AM | Invitrogen | M14206 | Prepared only in DMSO. Pluronic acid is not required and should not be used to avoid fiber deterioration. |
| Mercaptoethanol | Applichem | A11080100 | |
| Methanol | Protokimica | MP10043 | |
| Mice | Several | Several | For this manuscript, we only used C57BL/6 mice. However, some preliminary results have shown that the protocol works well for Swiss Webster mice of the same age and weight. |
| Mowiol 4-88 | Sigma Aldrich | 81381 | |
| N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethane-1,2-diamine (TEMED) | Promega | V3161 | |
| N-benzyl-p-toluene sulphonamide (BTS) | Tocris | 1870 | |
| Optimal cutting compound (OCT) | Thermo Scientific | 6769006 | |
| Secondary antibody | Thermo Scientific | A-11001 | Goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 |
| Sodium dodecil sulfate | Panreac | 1323631209 | |
| TRIS 0.5 M, pH 6.8 | AMRESCO | J832 | |
| Tris(Hydroxymethyl)aminomethane | AMRESCO | M151 | |
| Triton X-100 | AMRESCO | M143 | |
| Materials | |||
| Dissection chamber | Custom-made | ||
| Charged slides | Erie Scientific | 5951PLUS | |
| Experimental bath chamber | Warner Instruments | RC-27NE2 | Narrow Bath Chamber with Field Stimulation, ensembled on a heated platform PH-6 |
| Fine forceps | World Precision Instruments | 500338, 500230 | |
| Fine scissors | World Precision Instruments | Vannas Scissors 501778 | |
| Glass Pasteur pipettes | Several | Fire-polished tips | |
| Glass vials with cap | Several | 2-3 mL volumen | |
| Operating scissors | World Precision Instruments | 501223-G | |
| Equipment | |||
| Centrifuge | Thermo Scientific | SL 8R | |
| Confocal microscope | Olympus | FV1000 | |
| Cryostat | Leica | CM1850 | |
| Digital camera | Zeiss | Erc 5s and Axio 305 | Axio 305, coupled to the Stemi 508 stereoscope, was used to take pictures during dissection; while Erc 5s or Axio 208, coupled to the Axio Observer A1 microscope, were used to take images of the isolated fibers and the immunofluorescence assays |
| Digitizer | Molecular Devices | 1550A Digidata | |
| Electrophoresis chamber | Bio Rad | Mini-Protean IV | |
| Inverted microscope coupled to fluorescence | Zeiss | Axio Observer A1 | Coupled to an appropriate light source, filters and objectives for fluorescence |
| Photomultiplier | Horiba | R928 tube, Hamamatsu, in a D104 photometer, Horiba | Coupled to the lateral port of the fluorescence microscope |
| Stereoscope | Zeiss | Stemi 508 | |
| Stimulator | Grass Instruments | S6 | |
| Water bath | Memmert | WNE-22 | |
| Xilol | Sigma Aldrich | 808691 | |
| Software | |||
| Free software for electrophoreses analyses | University of Kentucky | GelBandFitter v1.7 | http://www.gelbandfitter.org |
| Free software for image analysis and morphometry | National Institutes of Health | ImageJ v1.54 | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/index.html |
| Licensed software for Ca2+ signals acquisition and analyses | Molecular Devices | pCLAMP v10.05 | https://www.moleculardevices.com |
| Licensed software for statistical analyses and graphing | OriginLab | OriginPro 2019 | https://www.originlab.com/ |
References
- Frontera, W. R., Ochala, J. Skeletal muscle: a brief review of structure and function. Calcif Tissue Int. 96 (3), 183-195 (2015).
- Barclay, C., Launikonis, B. Components of activation heat in skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 42 (1), 1-16 (2021).
- Gallo-Villegas, J. A., Calderón, J. C. Epidemiological, mechanistic, and practical bases for assessment of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle status in adults in healthcare settings. Eur J Appl Physiol. 123 (5), 945-964 (2023).
- Cardamone, M., Darras, B. T., Ryan, M. M. Inherited myopathies and muscular dystrophies. Semin Neurol. 28 (2), 250-259 (2008).
- Sánchez-Aguilera, P., et al. Role of ABCA1 on membrane cholesterol content, insulin-dependent Akt phosphorylation and glucose uptake in adult skeletal muscle fibers from mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863 (12), 1469-1477 (2018).
- Cruz-Jentoft, A. J., et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 48 (1), 16-31 (2019).
- Narvaez-Sanchez, R., Calderón, J. C., Vega, G., Trillos, M. C., Ospina, S. Skeletal muscle as a protagonist in the pregnancy metabolic syndrome. Med Hypotheses. 126, 26-37 (2019).
- Gallo-Villegas, J., et al. Efficacy of high-intensity interval- or continuous aerobic-training on insulin resistance and muscle function in adults with metabolic syndrome: a clinical trial. Eur J Appl Physiol. 122 (2), 331-344 (2022).
- Close, R. Properties of motor units in fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat. J Physiol. 193 (1), 45-55 (1967).
- Barnard, R. J., Edgerton, V. R., Furukawa, T., Peter, J. B. Histochemical, biochemical, and contractile properties of red, white, and intermediate fibers. Am J Physiol. 220, 410-414 (1971).
- Bär, A., Pette, D. Three fast myosin heavy chains in adult rat skeletal muscle. FEBS letters. 235 (1-2), 153-155 (1988).
- Schiaffino, S., et al. Myosin heavy chain isoforms and velocity of shortening of type 2 skeletal muscle fibres. Acta Physiol Scand. 134 (4), 575-576 (1988).
- Schiaffino, S., et al. Three myosin heavy chain isoforms in type 2 skeletal muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 10 (3), 197-205 (1989).
- Ranatunga, K., Thomas, P. Correlation between shortening velocity, force-velocity relation and histochemical fibre-type composition in rat muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 11 (3), 240-250 (1990).
- Hämäläinen, N., Pette, D. The histochemical profiles of fast fiber types IIB, IID, and IIA in skeletal muscles of mouse, rat, and rabbit. J Histochem Cytochem. 41 (5), 733-743 (1993).
- Agbulut, O., Li, Z., Mouly, V., Butler-Browne, G. S. Analysis of skeletal and cardiac muscle from desmin knock-out and normal mice by high resolution separation of myosin heavy-chain isoforms. Biol Cell. 88 (3), 131-135 (1996).
- Bekoff, A., Betz, W. Properties of isolated adult rat muscle fibres maintained in tissue culture. J Physiol. 271 (2), 537-547 (1977).
- Bekoff, A., Betz, W. Physiological properties of dissociated muscle fibres obtained from innervated and denervated adult rat muscle. J Physiol. 271 (1), 25-40 (1977).
- Schuetze, S. M. The acetylcholine channel open time in chick muscle is not decreased following innervation. J Physiol. 303, 111-124 (1980).
- Youhanna, S., Bruton, J., Jardemark, K., Westerblad, H., Lauschke, V. M. Calcium measurements in enzymatically dissociated or mechanically microdissected mouse primary skeletal muscle fibers. STAR Protoc. 4 (2), 102260(2023).
- Wozniak, A. C., Anderson, J. E. Single-fiber isolation and maintenance of satellite cell quiescence. Biochem Cell Biol. 83 (5), 674-676 (2005).
- Anderson, J. E., Wozniak, A. C., Mizunoya, W. Single muscle-fiber isolation and culture for cellular, molecular, pharmacological, and evolutionary studies. Methods Mol Biol. 798, 85-102 (2012).
- Bolaños, P., Guillen, A., Gámez, A., Caputo, C. Quantifying SOCE fluorescence measurements in mammalian muscle fibres. The effects of ryanodine and osmotic shocks. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 34 (5-6), 379-393 (2013).
- Lopez, R., et al. Raptor ablation in skeletal muscle decreases Cav1.1 expression and affects the function of the excitation-contraction coupling supramolecular complex. Biochem J. 466 (1), 123-135 (2015).
- Tarpey, M. D., et al. Characterization and utilization of the flexor digitorum brevis for assessing skeletal muscle function. Skelet Muscle. 8 (1), 14(2018).
- Milán, A. F., et al. Calibration of mammalian skeletal muscle Ca2+ transients recorded with the fast Ca2+ dye Mag-Fluo-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1865 (9), 129939(2021).
- Park, K. H., et al. Assessment of calcium sparks in intact skeletal muscle fibers. J Vis Exp. (84), e50898(2014).
- Wei-LaPierre, L., Groom, L., Dirksen, R. T. Acute exposure to extracellular BTP2 does not inhibit Ca2+ release during EC coupling in intact skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 154 (9), 202112976(2022).
- Banks, Q., et al. Voltage sensor movements of Ca(V)1.1 during an action potential in skeletal muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 118 (40), 2026116118(2021).
- Jaque-Fernandez, F., et al. Preserved Ca2+ handling and excitation-contraction coupling in muscle fibres from diet-induced obese mice. Diabetologia. 63 (11), 2471-2481 (2020).
- Ravenscroft, G., et al. Dissociated flexor digitorum brevis myofiber culture system--a more mature muscle culture system. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 64 (10), 727-738 (2007).
- Leduc-Gaudet, J. -P., et al. MYTHO is a novel regulator of skeletal muscle autophagy and integrity. Nat Commun. 14 (1), 1199(2023).
- Calderón, J. C., Bolaños, P., Caputo, C. Myosin heavy chain isoform composition and Ca2+ transients in fibres from enzymatically dissociated murine soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscles. J Physiol. 588 (1), 267-279 (2010).
- Calderón, J. C., Bolaños, P., Caputo, C. Kinetic changes in tetanic Ca2+ transients in enzymatically dissociated muscle fibres under repetitive stimulation. J Physiol. 589 (21), 5269-5283 (2011).
- Calderón, J. C., Bolaños, P., Caputo, C. Tetanic Ca2+ transient differences between slow- and fast-twitch mouse skeletal muscle fibres: a comprehensive experimental approach. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 35 (5-6), 279-293 (2014).
- Li, R., et al. Development of a high-throughput method for real-time assessment of cellular metabolism in intact long skeletal muscle fibre bundles. J Physiol. 594 (24), 7197-7213 (2016).
- Chemello, F., et al. Microgenomic analysis in skeletal muscle: expression signatures of individual fast and slow myofibers. PloS One. 6 (2), 16807(2011).
- Williams, D. A., Head, S. I., Bakker, A. J., Stephenson, D. G. Resting calcium concentrations in isolated skeletal muscle fibres of dystrophic mice. J Physiol. 428 (1), 243-256 (1990).
- Pasut, A., Jones, A. E., Rudnicki, M. A. Isolation and culture of individual myofibers and their satellite cells from adult skeletal muscle. J Vis Exp. (73), e50074(2013).
- Brun, C. E., et al. GLI3 regulates muscle stem cell entry into G(Alert) and self-renewal. Nat Commun. 13 (1), 3961(2022).
- Percie du Sert, N., et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: updated guidelines for reporting animal research. J Physiol. 598 (18), 3793-3801 (2020).
- Charles, J. P., Cappellari, O., Spence, A. J., Hutchinson, J. R., Wells, D. J. Musculoskeletal geometry, muscle architecture and functional specialisations of the mouse hindlimb. PLoS One. 11 (4), 0147669(2016).
- Enríquez, V., Granados, S., Arias, M. P., Calderón, J. C. Muscle fiber types of gluteus medius in the Colombian creole horse. J Equine Vet Sci. 35 (6), 524-530 (2015).
- Sartorius, C. A., et al. Myosin heavy chains IIa and IId are functionally distinct in the mouse. J Cell Biol. 141 (4), 943-953 (1998).
- Talmadge, R. J., Roy, R. R. Electrophoretic separation of rat skeletal muscle myosin heavy-chain isoforms. J Appl Physiol. 75 (5), 2337-2340 (1993).
- Hämäläinen, N., Pette, D. Patterns of myosin isoforms in mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. Microsc Res Tech. 30 (5), 381-389 (1995).
- Bolaños, P., Calderón, J. C. Excitation-contraction coupling in mammalian skeletal muscle: Blending old and last-decade research. Front Physiol. 13, 989796(2022).
- Gineste, C., et al. Enzymatically dissociated muscle fibers display rapid dedifferentiation and impaired mitochondrial calcium control. iScience. 25 (12), 105654(2022).
- Calderón, J. C., Bolaños, P., Caputo, C. The excitation-contraction coupling mechanism in skeletal muscle. Biophys Rev. 6 (1), 133-160 (2014).
- Lainé, J., Skoglund, G., Fournier, E., Tabti, N. Development of the excitation-contraction coupling machinery and its relation to myofibrillogenesis in human iPSC-derived skeletal myocytes. Skelet Muscle. 8 (1), (2018).
- Rao, L., Qian, Y., Khodabukus, A., Ribar, T., Bursac, N. Engineering human pluripotent stem cells into a functional skeletal muscle tissue. Nat Commun. 9 (1), 126(2018).
- Cea, L. A., et al. The absence of dysferlin induces the expression of functional connexin-based hemichannels in human myotubes. BMC Cell Biology. 17 (15), 127-136 (2016).
- Nakada, T., et al. Physical interaction of junctophilin and the Ca(V)1.1 C terminus is crucial for skeletal muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 115 (17), 4507-4512 (2018).
- Cully, T. R., Edwards, J. N., Murphy, R. M., Launikonis, B. S. A quantitative description of tubular system Ca2+ handling in fast- and slow-twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 594 (11), 2795-2810 (2016).
- Lim, J. -Y., Frontera, W. R. Single skeletal muscle fiber mechanical properties: a muscle quality biomarker of human aging. Eur J Appl Physiol. 122 (6), 1383-1395 (2022).
- Gonzalez, E., Messi, M. L., Zheng, Z., Delbono, O. Insulin-like growth factor-1 prevents age-related decrease in specific force and intracellular Ca2+ in single intact muscle fibres from transgenic mice. J Physiol. 552, 833-844 (2003).
- Luedeke, J. D., McCall, R. D., Dillaman, R. M., Kinsey, S. T. Properties of slow- and fast-twitch skeletal muscle from mice with an inherited capacity for hypoxic exercise. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 138 (3), 373-382 (2004).
- Asmussen, G., Schmalbruch, I., Soukup, T., Pette, D. Contractile properties, fiber types, and myosin isoforms in fast and slow muscles of hyperactive Japanese waltzing mice. Exp Neurol. 184 (2), 758-766 (2003).
- Augusto, V., Padovani, C. R., Campos, G. E. R. Skeletal muscle fiber types in C57BL6J mice. Braz J Morphol Sci. 21 (2), 89-94 (2004).
- Wang, L. C., Kernell, D. Fibre type regionalisation in lower hindlimb muscles of rabbit, rat and mouse: a comparative study. J Anat. 199, 631-643 (2001).
- Abbassi-Daloii, T., et al. Quantitative analysis of myofiber type composition in human and mouse skeletal muscles. STAR Protoc. 4 (1), 102075(2023).
- Tulloch, L. K., Perkins, J. D., Piercy, R. J. Multiple immunofluorescence labelling enables simultaneous identification of all mature fibre types in a single equine skeletal muscle cryosection. Equine Vet J. 43 (4), 500-503 (2011).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved