A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Identification and Analysis of Myogenic Progenitors In Vivo During Acute Skeletal Muscle Injury by High-Dimensional Single-Cell Mass Cytometry
In This Article
Summary
The protocol presented here enables the identification and high-dimensional analysis of muscle stem and progenitor cells by single-cell mass cytometry and their purification by FACS for in-depth studies of their function. This approach can be applied to study regeneration dynamics in disease models and test the efficacy of pharmacological interventions.
Abstract
Skeletal muscle regeneration is a dynamic process driven by adult muscle stem cells and their progeny. Mostly quiescent at a steady state, adult muscle stem cells become activated upon muscle injury. Following activation, they proliferate, and most of their progeny differentiate to generate fusion-competent muscle cells while the remaining self-renews to replenish the stem cell pool. While the identity of muscle stem cells was defined more than a decade ago, based on the co-expression of cell surface markers, myogenic progenitors were identified only recently using high-dimensional single-cell approaches. Here, we present a single-cell mass cytometry (cytometry by time of flight [CyTOF]) method to analyze stem cells and progenitor cells in acute muscle injury to resolve the cellular and molecular dynamics that unfold during muscle regeneration. This approach is based on the simultaneous detection of novel cell surface markers and key myogenic transcription factors whose dynamic expression enables the identification of activated stem cells and progenitor cell populations that represent landmarks of myogenesis. Importantly, a sorting strategy based on detecting cell surface markers CD9 and CD104 is described, enabling prospective isolation of muscle stem and progenitor cells using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) for in-depth studies of their function. Muscle progenitor cells provide a critical missing link to study the control of muscle stem cell fate, identify novel therapeutic targets for muscle diseases, and develop cell therapy applications for regenerative medicine. The approach presented here can be applied to study muscle stem and progenitor cells in vivo in response to perturbations, such as pharmacological interventions targeting specific signaling pathways. It can also be used to investigate the dynamics of muscle stem and progenitor cells in animal models of muscle diseases, advancing our understanding of stem cell diseases and accelerating the development of therapies.
Introduction
Skeletal muscle constitutes the largest tissue by mass in the body and regulates multiple functions, from eyesight to respiration, from posture to movement, as well as metabolism1. Therefore, maintaining skeletal muscle integrity and function is critical to health. Skeletal muscle tissue, which consists of tightly packed bundles of multinucleated myofibers surrounded by a complex network of nerves and blood vessels, exhibits remarkable regenerative potential1,2.
The main drivers of skeletal muscle regeneration are adult muscle stem cells (MuSCs). Also known as satellite cells, due to their unique anatomical location adjacent to the plasma membrane of the myofiber and beneath the basal lamina, they were first identified in 19613. MuSCs express a unique molecular marker, the transcription factor paired box 7 (Pax7)4. Mostly quiescent in healthy adults, they become activated upon muscle injury and proliferate to give rise to progeny that will (i) differentiate into fusion-competent muscle cells that will form new myofibers to repair muscle damage or (ii) self-renew to replenish the stem cell pool5.
At the cellular and molecular level, the process of regeneration is quite dynamic and involves cell-state transitions, characterized by the coordinated expression of key myogenic transcription factors, also known as myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs)6,7. Prior in vivo developmental studies, lineage tracing experiments, and cell culture work using myoblasts have shown that sequential expression of these transcription factors drives myogenesis, with myogenic factor 5 (Myf5) being expressed upon activation, myogenic differentiation 1 (MyoD1) expression marking commitment to the myogenic program, and myogenin (MyoG) expression marking differentiation8,9,10,11,12,13,14. Despite this knowledge and the discovery of cell surface markers to purify MuSCs, strategies and tools to identify and isolate discrete populations along the myogenic differentiation path and resolve a myogenic progression in vivo have been lacking15,16,17,18.
Here, we present a novel method, based on recently published research, which enables the identification of stem and progenitor cells in skeletal muscle and the analysis of their cellular, molecular, and proliferation dynamics in the context of acute muscle injury19. This approach relies on single-cell mass cytometry (also known as Cytometry by Time of Flight [CyTOF]) to simultaneously detect key cell surface markers (α7 integrin, CD9, CD44, CD98, and CD104), intracellular myogenic transcription factors (Pax7, Myf5, MyoD, and MyoG) and a nucleoside analog (5-Iodo-2′-deoxyuridine, IdU), to monitor cells in S phase19,20,21,22,23. Moreover, the protocol presents a strategy based on the detection of two cell surface markers, CD9 and CD104, to purify these cell populations by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), therefore enabling future in-depth studies of their function in the context of injury and muscle diseases. While primary myoblasts have been extensively used in the past to study the late stages of myogenic differentiation in vitro, it is not known whether they recapitulate the molecular state of muscle progenitor cells found in vivo24,25,26,27,28,29,30. The production of myoblasts is laborious and time-consuming, and the molecular state of this primary culture changes rapidly upon passaging31. Hence, freshly isolated myogenic progenitors purified with this method will provide a more physiological system to study myogenesis and the effect of genetic or pharmacological manipulations ex-vivo.
The protocol presented here can be applied to address a variety of research questions, for example, to study the dynamics of the myogenic compartment in vivo in animal models of muscle diseases, in response to acute genetic manipulations or upon pharmacological interventions, therefore deepening our understanding of muscle stem cell dysfunction in different biological contexts and facilitating the development of novel therapeutic interventions.
Protocol
Animal procedures were approved by the Danish animal experiments inspectorate (protocol # 2022-15-0201-01293), and experiments were performed in compliance with the institutional guidelines of Aarhus University. Analgesia (buprenorphine) is provided in drinking water 24 h prior to injury for the mice to adapt to the taste. Supplying buprenorphine in drinking water is continued for 24 h post-injury. Together with a subcutaneous (s.c.) injection of buprenorphine at the time of acute muscle injury, buprenorphine in the drinking water after notexin injection will alleviate the pain associated with the injury. While it is recommended to administer a s.c. injection of buprenorphine at the time of acute muscle injury, followed by buprenorphine in the drinking water, buprenorphine in the drinking water prior to injury is optional. However, researchers must follow the animal welfare standards and guidelines established by the appropriate regulatory agency.
NOTE: For single-cell mass cytometry (CyTOF) experiments of injured hindlimb muscles, start at section 1: Analgesia in water 24 h prior to muscle injury until 24 h post-injury. For sorting of muscle stem and progenitor cells from uninjured mice, perform sections 5 and 6: Euthanasia + Skeletal muscle dissection and dissociation, and continue to section 11: Staining with fluorophore-conjugated antibodies for FACS. An overview of the experimental setup and the protocol is shown in Figure 1.
1. Analgesia in water 24 h prior to muscle injury until 24 h post-injury
- To a dark or aluminum foil wrapped drinking bottle, add 3 mL of buprenorphine (0.3 mg/mL) and fill to 100 mL with filtered water to reach a final concentration of 0.009 mg/mL 24 h pre-injury. Attach to the mouse cage.
- Remove the drinking bottle 24 h post-injury, and reconnect the mouse cage to the drinking valve system.
2. Preparing for acute injury procedure
NOTE: Use 70% ethanol to disinfect the work bench, nose cone setup and induction box.
- Prepare a 1.5 mL tube with diluted notexin in PBS (5 µg/mL). Dilute buprenorphine (0.3 mg/mL) in sterile 0.9% saline to 0.015 mg/mL in a light-safe 1.5 mL tube. Keep on ice. Prepare insulin syringes for buprenorphine (28 G, 0.5 mL) and notexin injections (29 G, 0.3 mL).
- Configure isoflurane-based anesthetic units:
- For anesthesia in an induction box, use 3% isoflurane with a flow of 1.5 L/min (50% O2, 50% atmospheric air).
- For maintenance utilizing a nose cone setup, use 1.5% isoflurane with a flow of 0.6 L/min (50% O2, 50% atmospheric air).
3. Acute injury by notexin injection
CAUTION: Notexin has Phospholipase A2 activity and is the principal component of venom from the Australian tiger snake (Notechis scutatus), with an intravenous LD50 of 5–17 mg notexin/kg in mice32,33. In the present protocol, the Tibialis Anterior (TA) muscle of each hindlimb is injected with 10 µL of 5 mg/mL notexin, and the Gastrocnemius (GA) muscle of each hindlimb is injected twice (once into each head of the muscle) with 15 µL of 5 mg/mL notexin. It is important to perform the intramuscular (i.m.) injections correctly to limit damage and frequently inspect the injected animals to ensure minimal pain.
- Anesthetize the mouse in the induction box (3% isoflurane). When the mouse is unconscious, lower the isoflurane level to 1.5% in the induction box.
- Weigh and individually mark the mice according to institutional approved procedures. Under the nose cone setup, shave the hindlimbs with a trimmer and transfer back to the induction box.
- Calculate buprenorphine volume for each mouse :
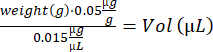
- Mix the notexin solution by pipetting up and down. Prepare 2 insulin syringes (29 G, 0.3 mL) loaded with 10 µL of notexin solution (5 µg/mL) for TA injections, and 4 insulin syringes loaded with 15 µL of notexin solution (5 µg/mL) for GA injection.
NOTE: The Tibialis Anterior (TA) muscle is located on the anterior side of the lower leg of the mouse, extending from the knee to the ankle. The Gastrocnemius (GA) muscle is a two-headed muscle that is located in the back of the lower leg, superficial to the soleus. It runs from its two heads (medial and lateral) just above the knee to the heel, extending across a total of three joints (knee, ankle, and subtalar joints). - Perform intramuscular injections
- TA injection (2 injections in total)
- Place the mouse in a supine position under the nose cone setup and disinfect the injection site with sterile alcohol wipes (70% ethanol or isopropanol). Insert the needle, bevel down, in the belly of the TA (distal to the mid-belly) at 30° angle. Advance the needle along the muscle, moving parallel to the tibia, to reach the mid-belly of the TA. Inject the notexin slowly and continuously, leaving the needle in place for 10 s before withdrawing it. Do not insert the needle too deep initially (to avoid injecting notexin below the TA into the extensor digitorum longus muscle), and not too far proximally when advancing the needle (to avoid injecting too close to the knee).
- GA injection (4 injections in total)
- Insert the needle, bevel down, at ~45° angle in the mid-belly of the lateral head of the GA. Inject the notexin slowly and continuously, leaving the needle in place for 10 s before withdrawing it. Rotate the hindlimb and inject notexin in the medial head of the GA muscle as above. Care should be taken not to insert the needle too deeply.
- TA injection (2 injections in total)
- Turn the mouse around and inject buprenorphine s.c. using an insulin syringe (28 G, 0.5 mL). Transfer the mouse to an empty recovery cage on a heating plate. Only half of the cage bottom should be placed over the heating plate to allow the mouse to thermoregulate during recovery34. Repeat steps 3.3–3.6 for the remaining mice.
- When the mouse in the recovery cage is fully awake, move it back into the original cage. Return it to the stable and supplement it with wetted chow. Remove the buprenorphine drinking bottle 24 h after injection.
- Monitor the mice for 6 h after notexin injection and then every 12 h for 2 days for signs of pain, impaired mobility, and decreased food consumption35,36.
4. 5-Iodo-2’-deoxyuridine injection
CAUTION: 5-Iodo-2’-deoxyuridine (IdU) is suspected of causing genetic defects and damaging fertility or the unborn child. Read the safety data sheet (SDS) before handling. Personal protective equipment should be worn during handling. Use a fume hood when weighing the IdU powder. Materials that have been in contact with IdU should be discarded according to local safety regulations.
NOTE: IdU labeling in vivo is used to monitor cell division during the injury time course because IdU, an iodinated thymidine analog, gets incorporated into the DNA of cells in S phase. IdU is injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) at 20 mg/kg body weight 8 h prior to sacrificing the mouse.
- Use a sonicator at 37 °C to prepare a 2 mg/mL stock solution of IdU in sterile PBS. IdU is light-sensitive; use within the same day or freeze at -20 °C for up to 3 months. If using frozen IdU: thaw, vortex, centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 30 s, and use the supernatant for injections below.
- Anesthetize the mouse in the induction box (3% isoflurane). Note earmarking, weigh the mice, and calculate the volume of the IdU solution:
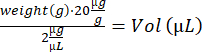
- Perform i.p. injection using an insulin syringe (28 G, 0.5 mL) and transfer the mouse to an empty recovery cage on a heating plate. When awake, move the mouse back to its original cage. Repeat steps 4.2–4.3 for the remaining mice and return them to the stable.
5. Euthanasia
NOTE: See Table 1 for buffer recipes. Prepare wash media (Nutrient mixture F-10 (Ham's), 10% horse serum, 1x Pen/Strep) and filter through a polyethersulfone (PES) membrane into a polystyrene container. Prepare dissociation buffer (wash media supplemented with 650 U/mL Collagenase, Type II) and keep on ice. CyTOF mass cytometry measurements are very sensitive to contaminants. For this reason, it is essential to use reagents of the highest analytical grade for sample processing. To prevent metal contamination, it is highly recommended to use sterile plasticware and new glassware that has never been washed with detergent because many laboratory soaps contain high levels of barium. It is recommended to use double-filtered, distilled, deionized water for reagent preparation. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) is prepared in-house. Dilute the 10x stocks to 1x and filter the 1x PBS with 0.2 μm filters. Filter the 1x PBS again at the start of each experiment. Dissection tools must not be cleaned with detergent due to the presence of barium.
- Prepare the weighing scale, container, and isoflurane-based anesthetic unit with the induction box. Disinfect appropriate dissection tools.
- Prepare and mark 50 mL tubes for each mouse with 5 mL of dissociation buffer and a Petri dish. Keep dissociation buffer on ice.
- Anesthetize the mouse in the induction box (3% isoflurane, increase to 5% when unconscious) and perform cervical dislocation.
6. Skeletal muscle dissection and dissociation
- Dissect TA and GA muscles from both hindlimbs and transfer into the lid of a Petri dish. Use scissors to cut the tissue into a minced slurry (~1 mm3 pieces). Transfer to a 50 mL tube containing 5 mL of ice-cold dissociation buffer. Keep on ice.
- Repeat the euthanasia procedure (step 5.3) and skeletal muscle dissection and dissociation procedure (step 6.1) until all mice have been processed.
- Pre-heat all sample tubes in a 37 °C water bath (2 min), and incubate for 45 min on rotation in an incubator (37 °C).
- Vortex and wash by adding 10 mL of wash media. Centrifuge (380 x g, 10 min, room temperature [RT]), and aspirate to 4 mL.
- Add 0.5 mL of collagenase (1000 U/mL) and 0.5 mL of dispase (11 U/mL). Vortex and incubate for 20 min on rotation at 37 °C (e.g., in an incubator). Centrifuge (380 x g, 1 min, RT) and resuspend with a 5 mL pipette.
- Add 40 µm cell strainers to 50 mL tubes and pre-wet with 5 mL of wash media. Aspirate and eject cell suspension 10 times using a 5 mL syringe with a 20 G needle. Strain through the pre-wetted 40 µm cell strainer. Wash the 50 mL tube with 10 mL wash media, transfer it to the 40 µm cell strainer, and centrifuge (380 x g, 10 min, 4 °C) the cell suspension.
7. Live/dead staining with cisplatin and paraformaldehyde fixation
CAUTION: Cisplatin and paraformaldehyde (PFA) are carcinogenic. Read the SDS before handling. Paraformaldehyde (PFA; 16%) is a skin, eye, and respiratory irritant. Wear personal protective equipment and handle these substances under a fume hood. During fixation of cells, the final concentration of PFA will be 1.6%. Correct protective measures should be taken, and waste should be handled according to local regulations.
NOTE: Prepare cold (4 °C) and warm (37 °C) serum-free DMEM. Prepare DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, filter through a PES membrane into a polystyrene container, and keep on ice. Prepare PBS and cell stain media (CSM; PBS, 0.5% BSA, 0.02% sodium azide) in a CyTOF-dedicated glass bottle and filter through a PES membrane. CSM can be stored at 4 °C for up to 6 months.
- Aspirate the supernatant, flick the pellet, and resuspend in 1 mL of cold serum-free DMEM. Count the cells and adjust the cell density to 1 x 106 cells/mL in serum-free DMEM.
- Add cisplatin stock (25 mM) to a final concentration of 25 µM. Vortex 10 s and incubate for exactly 1 min (the reaction is very time-sensitive). Quench the reaction with ice-cold DMEM+10% FBS (3 times the sample volume) and keep it on ice. Centrifuge (380 x g, 10 min, 4 °C), aspirate the supernatant and resuspend the pellet thoroughly (up to 10 x 106 cells/mL in CSM). Filter the suspension through a 35 µm cell strainer.
- Fix the cell suspension with filtered PFA stock solution (16%) and pipette up and down (perform under a fume hood) to reach the final PFA concentration (1.6%) (e.g., add 100 µL of 16% PFA to 900 µL of cell suspension). Vortex for 30 s, incubate for 10 min on ice, and wash twice with 2 mL of CSM by centrifugation (800 x g, 5 min, RT).
NOTE: At this point, the samples can either be snap-frozen on dry ice and stored at -80 °C or used directly for antibody staining. If cells are to be frozen, transfer cells into 5 mL polypropylene tubes, as polystyrene can crack at low temperatures. If freshly fixed cells are used for staining, proceed to step 8.2.
8. Staining with metal-conjugated antibodies
CAUTION: Methanol (MeOH) is highly flammable and corrosive to the respiratory tract. Read the SDS before handling. Wear personal protective equipment and handle this substance under a fume hood. Handle waste in accordance with local regulations.
NOTE: List of antibodies (Ab) targeting surface markers and intracellular markers can be found in Table 2.
Antibody conjugation: Most of the antibodies used in this protocol were conjugated in-house because they were not commercially available. Protocols for metal conjugation of antibodies have been previously published, and conjugation kits are now commercially available37,38. Immunoglobulin type G (IgG) is compatible with the available conjugation protocols. It is of high importance that the antibody formulation used for metal conjugation is free of cysteine-containing carrier proteins (e.g., bovine serum albumin (BSA)), which can affect conjugation efficiency by competing for the free maleimide groups of the polymer, and can interfere with quantification of the metal-conjugated antibody. The cysteine content of gelatin is much lower than that of BSA. However, it is recommended that if the antibody formulation contains carrier proteins, such proteins are removed prior to conjugation. It is now possible to request BSA- and gelatin-free antibodies from the manufacturer. Small molecule preservatives (e.g., sodium azide, glycerol, and trehalose) are compatible with metal conjugation protocols37,38.
Antibody titration: After each metal conjugation, antibodies should be titrated to determine the optimal antibody concentration that provides the maximal signal-to-noise ratio. For antibody titration, perform a 6-step two-fold serial dilution and stain both samples known to express (e.g., muscle cells, positive controls) and lack (negative controls) the protein of interest19,21,37,38.
Prepare fresh Cell-ID Intercalator-Ir (stock = 500 μM; intercalator-ir solution) working solution by diluting the stock to 0.1 μM in PBS/1.6% PFA.
- Thaw frozen samples for 5 min at RT and centrifuge (800 x g, 1 min, RT). Wash with 2 mL of CSM by centrifugation (800 x g, 5 min, RT).
- Prepare a 2.5x surface antibody (Ab) staining mix in CSM. Aspirate the supernatant to ~60 µL and resuspend the pellet thoroughly. Stain the cells by adding 40 µL of surface Ab staining mix and incubating it for 1 h at RT.
- Flick the samples every 20 min to mix. Wash twice with 1 mL of CSM by centrifugation (800 x g, 5 min, RT). Aspirate the supernatant and flick the pellet.
NOTE: If no intracellular staining is needed, methanol permeabilization is not required. However, if only surface staining is performed, the intercalator-ir solution has to be diluted in a buffer containing a permeabilizing agent (e.g., Maxpar fix and perm buffer) to penetrate the nuclear membrane. Proceed to step 8.5 and dilute the Cell-ID Intercalator-Ir in a buffer containing a permeabilizing agent and 1.6% PFA. Otherwise, continue with the intracellular staining below.
CAUTION: Iridium is hazardous, and precautions for safe handling must be taken. Iridium is flammable and is an irritant to the eyes/skin. Avoid creating and breathing dust or fumes. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. However, the intercalator-ir solution mixture is provided at a concentration of <1% in water, which is considered non-hazardous according to the globally harmonized system (GHS) of classification and labeling of chemicals. Read the SDS from Standard Biotools before handling. Personal protective equipment should be worn during handling. Materials that have been in contact with the intercalator-ir solution should be discarded according to local safety regulations. - To permeabilize the cells, add 0.5 mL of ice-cold MeOH dropwise while vortexing. Incubate for 15 min on ice under a fume hood. Centrifuge (800 x g, 5 min, RT) and then wash twice with 1 mL of CSM by centrifugation (800 x g, 5 min, RT). After the last wash, aspirate the supernatant to ~60 µL and resuspend the pellet thoroughly.
- Prepare a 2.5x intracellular Ab staining mix in CSM. Stain the cells by adding 40 µL of intracellular Ab staining mix and incubating for 1 h at RT. Flick the samples every 20 min to mix.
- Wash twice with 1 mL of CSM by centrifugation (800 x g, 5 min, RT). Aspirate the supernatant and flick the pellet. Resuspend the samples in 0.5 mL of intercalator-iridium solution (Table 1) and vortex. Incubate the samples for 1 h at RT or overnight (O/N) at 4 °C (see note below).
NOTE: Samples can be stored in intercalator-iridium solution at 4 °C for up to 48 h. The staining protocol used in this study has been developed based on pioneering work by the Nolan lab{C}23. It differs from the Standard Biotools protocols, as (i) in-house prepared buffers are used for washing and staining, (ii) the cells are fixed prior to surface staining, and (iii) cells are permeabilized with methanol for intracellular staining with antibodies to transcription factors or signaling molecules. Researchers developing a new protocol must thoroughly test the compatibility of their antibody panel with methanol as a permeabilization agent. When adding new antibodies to a panel, it is recommended to test antibody specificity by flow cytometry using positive and negative control samples prior to metal conjugation and titration.
9. Sample preparation for loading into mass cytometer
NOTE: Cell pellets are very loose when in CAS buffer (Table of Materials). During washes with CAS buffer, do not aspirate to dryness. Instead, keep a residual volume as described below.
- Vortex and centrifuge (800 x g, 10 min, RT) the samples. Pour off the supernatant (handle as PFA waste) and vortex.
- Wash with 1 mL of CSM by centrifugation (800 x g, 10 min, RT). Aspirate the supernatant and flick the pellet.
- Wash with 1 mL of CAS buffer by centrifugation (800 x g, 10 min, RT). Aspirate to ~200 µL. Vortex and add 1 mL of CAS buffer. Take out 5 µL aliquot for cell count. Centrifuge (800 x g, 10 min, RT) and carefully aspirate to ≤50 µL. Do not disturb the pellet.
- Resuspend the pellet to 1–2 x 106 cells/mL in CAS buffer and add calibration beads (1x; Table of Materials) to a final concentration of 0.1x (e.g., add 100 µL of 1x calibration beads to 900 µL of cell suspension).
- Load the sample into the mass cytometer and collect data using a flow rate of 400–500 cells/s.
- Perform data normalization of FCS files using the CyTOF software or previously developed normalization tools39.
NOTE: Operation of CyTOF mass cytometers is instrument-specific40,41. It is recommended to consult the CyTOF user manual prior to operation. The calibration beads are metal-embedded polystyrene normalization bead standards containing known concentrations of the metal isotopes cerium (140/142Ce), europium (151/153Eu), holmium (165Ho), and lutetium (175/176Lu). The calibration beads allow for control for machine sensitivity, which can vary over time, primarily due to the buildup of biological material and variations in plasma ionization over time.
10. CyTOF data analysis
NOTE: For downstream analysis, normalized FCS files can be analyzed locally or uploaded to cloud-based software solutions such as Cytobank, Cell Engine, OMIQ, or FCS Express42.
- Concatenate individual FCS files for each sample into a single file, if necessary.
- Identify single cells by gating on Iridium-intercalator positive events, which enables discrimination of single nucleated cells from debris or doublets.
- Gate for live cells by selecting cisplatin negative events. Cisplatin binds covalently to cellular proteins and labels dying and dead cells with compromised membranes to a greater extent than live cells43.
- Gate on the population of interest, for example, the myogenic compartment (Live/CD45-/CD31-/Sca1-/α7integrin+/CD9+) (Figure 2A) and quantify the relative proportion of stem and progenitor cells. This approach requires prior knowledge of cell surface or intracellular marker expression to define individual populations.
- To perform high-dimensional analysis that will enable the identification of previously unrecognized rare cell subsets within a complex population, export the population of interest, and use clustering algorithms that have been developed specifically for CyTOF data analysis44.
NOTE: Previous work employed the X-shift algorithm, which uses weighted k-nearest neighbor density estimation (kNN-DE) in high-dimensional space to perform unsupervised clustering based on defined parameters19. X-shift has been shown to be highly effective in identifying rare cell populations45. - For X-shift analysis, download the vortex software package (from the Nolan lab GitHub page [https://github.com/nolanlab/vortex]) and Java 64-bit46. Instructions can be found here: https://github.com/nolanlab/vortex/wiki/Getting-Started.
- Upload the exported cell populations to a local database and define the clustering parameters. Among the user-defined parameters are (i) the markers used for clustering, (ii) the range of k values (e.g., 5 to 150), and (iii) the number of clustering steps.
NOTE: Previous work used, as clustering markers, a combination of surface markers known to be expressed in muscle stem cells, novel surface markers identified in a high throughput flow cytometric screen of muscle cells and myoblasts, and myogenic transcription factors (TFs) known to define different stages of myogenesis. This approach enabled the identification of two cell surface markers, CD9 and CD104, whose co-expression pattern distinguishes previously unrecognized progenitor cell populations19. The careful choice of clustering markers will allow the researcher to answer specific research questions. For example, if identification and analysis over time of dividing cell subsets is desired, including IdU as one of the clustering markers is recommended. X-shift can perform clustering at multiple k values and automatically identify, by calculating the “elbow point”, the k value that results in optimal cluster number, therefore avoiding under-clustering or over-fragmentation. It is recommended to calculate the elbow point and use the clustering analysis defined by the optimal k value for data visualization and downstream applications. - To visualize the spatial relationships between cell populations within the X-shift clusters, perform a force-directed layout, which will generate a 2D map where the distance between clusters indicates their similarity in marker expression in high dimensional phenotypic space. By coloring the map using one marker at a time, it is possible to discover novel cell populations and follow their dynamics. Follow-up quantification by manual gating in software, such as Cytobank and Cell Engine, is recommended.
- Perform heatmap analysis to quantify the dynamic expression of multiple surface and intracellular proteins throughout the time course and reveal new trends.
NOTE: When performing an injury time course, it is possible to cluster data from all time points together to generate a map of regeneration. In addition, it is possible to dissect such map into the individual time points to follow the cellular and molecular dynamics of regeneration over time19.
11. Staining with fluorophore-conjugated antibodies for FACS
NOTE: Cells used for unstained, single-color controls and fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls can originate from the TA and GA set from an extra mouse if available. Alternatively, the quadriceps (upper anterior thigh muscle) can be dissected and digested into a single cell suspension, following the same procedure as for the TA+GA set above and used for controls. Prepare FACS buffer (PBS, 2.5% Goat serum, 2 mM EDTA), filter through a PES membrane into a polystyrene container, and keep on ice. FACS buffer can be stored at 4 °C for up to 1 month. A list of antibodies used for FACS can be found in Table 3.
- Prepare a lineage mix. Stain each control in 50 µL (containing approx. 3–5 x 105 cells). Calculate the amount of lineage mix needed. Make 20%–30% volume excess. The stock concentration of antibodies used for the lineage mix is 0.2 mg/mL.
- In a 0.5 mL tube, add anti-CD45 APC-Cy7, anti-CD31 APC-Cy7, anti-Sca1 APC-Cy7, and anti-CD11b APC-Cy7 to reach final concentrations of 1 µg/mL, 2.5 µg/mL, 2.5 µg/mL, and 0.63 µg/mL, respectively.
- Prepare all-stain mix. Stain each all-stained sample in 500 µL (containing approx. 3–5 x 106 cells). Make 10% volume excess of all-stain-mix.
- In a 1.5 mL tube, add lineage-mix antibodies as above + anti-α7 integrin PE, anti-CD9 APC, and anti-CD104 FITC to reach final concentrations of 2 µg/mL, 1.2 µg/mL, and 3 µg/mL, respectively.
- Prepare FACS buffer + DAPI: For 10 mL of FACS buffer, add 1 µL of DAPI (stock = 1 mg/mL) to reach a 100 ng/mL final DAPI concentration.
CAUTION: DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride) is classified as a possible skin and respiratory irritant. However, DAPI solution at a concentration of <1% is considered non-hazardous, according to GHS. Read the SDS before handling. Personal protective equipment should be worn during handling. Materials that have been in contact with DAPI should be discarded according to local safety regulations. - Resuspend cells from section 6: Skeletal muscle dissection and dissociation:
- For all-stained samples, resuspend TA and GA sets from a single mouse in 500 µL of FACS buffer and transfer it to 15 mL tubes for staining.
- For controls, use either TA and GA sets or quadricep sets. If using 1 mouse for controls, resuspend cells in 750 µL of FACS buffer. If multiple mice, resuspend each TA and GA or quadricep set in 500 µL of FACS buffer and combine the sets into a single 1 mL sample by taking a fraction from each sample. Add 50 µL of control cells (3–5 x 105 cells) to 5 mL polypropylene tubes for staining.
- Stain as described in Table 4 for 45 min at 4 °C in the dark.
- Wash all-stained samples by adding 5 mL of FACS buffer. Wash the controls by adding 1 mL of FACS buffer and centrifuge (380 x g, 10 min, 4 °C).
- Resuspend all-stained samples in 1 mL of FACS buffer + DAPI. Resuspend the controls in 300 µL of FACS buffer with or without DAPI.
- Keep cells at 4 °C in the dark until sorting on a flow cytometer with 4 lasers (405 nm, 488 nm, 561 nm, 633 nm).
- Run the controls and samples on the sorter and create sorting gates using the relevant software. For unstained/single color controls and FMO controls, record 1 x 104 and 0.3–1 x 105 events, respectively. For all-stained samples, record up to 1 x 106 events. Sort all the all-stained samples, or as much as needed, depending on the downstream assay requirements. For the flow cytometer used here (FACSAria III), sort in Purity Mode using a 70 mm nozzle.
- See Figure 4 for the gating strategy.
- Use the unstained and single-color controls to set the voltage for all detectors.
- Use the single-color controls to set up the compensation matrix.
- Use the FMO controls to establish sorting gates.
- Distinct muscle stem and progenitor cell populations are sorted into ice-cold FACS buffer.
- Centrifuge (380 x g, 10 min, 4 °C) the cell populations. Resuspend in the appropriate buffer, count, and continue with downstream analysis.
Results
Here we present an overview of the experimental setup for using this combined approach which includes (i) high-dimensional CyTOF analysis of an acute injury time course by notexin injection to study the cellular and molecular dynamics of stem and progenitor cells in skeletal muscle (Figure 1, top scheme); and (ii) FACS of stem and progenitor cells using two cell surface markers, CD9 and CD104, to isolate these populations and perform in-depth studies of their function (F...
Discussion
Skeletal muscle regeneration is a dynamic process that relies on the function of adult stem cells. While prior studies have focused on the role of muscle stem cells during regeneration, their progeny in vivo has been understudied, primarily due to a lack of tools to identify and isolate these cell populations15,16,17,18. Here, we present a method to simultaneously identify and isolate ...
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the FACS Core Facility in the Department of Biomedicine at Aarhus University for technical support. We thank Alexander Schmitz, the manager of the Mass Cytometry Unit at the Department of Biomedicine, for discussion and support. Scientific Illustrations were created using Biorender.com. This work was funded by an Aarhus Universitets Forskningsfond (AUFF) Starting Grant and a Start Package grant (0071113) from Novo Nordisk Foundation to E.P.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 15 mL centrifuge tube | Fisher Scientific | 07-200-886 | |
| 20 G needle | KDM | KD-fine 900123 | |
| 28 G, 0.5 mL insulin syringe | BD | 329461 | |
| 29 G, 0.3 mL insulin syringe | BD | 324702 | |
| 3 mL syringes | Terumo medical | MDSS03SE | |
| 40 µm cell strainers | Fisher Scientific | 11587522 | |
| 5 mL polypropylene tubes | Fisher Scientific | 352002 | |
| 5 mL polystyrene test tubes with 35 µm cell strainer | Falcon | 352235 | |
| 5 mL syringes | Terumo medical | SS05LE1 | |
| 50 mL centrifuge tube | Fisher Scientific | 05-539-13 | |
| 5-Iodo-2-deoxyuridine (IdU) | Merck | I7125-5g | |
| anti-CD104 FITC (clone: 346-11A) | Biolegend | 123605 | Stock = 0.5 mg/mL |
| anti-CD11b APC-Cy7 (Clone: M1/70) | Biolegend | 101226 | Stock = 0.2 mg/mL |
| anti-CD31 APC-Cy7 (clone: 390) | Biolegend | 102440 | Stock = 0.2 mg/mL |
| anti-CD45 APC-Cy7 (Clone: 30-F11) | Biolegend | 103116 | Stock = 0.2 mg/mL |
| anti-CD9 APC (clone: KMC8) | ThermoFisher Scientific | 17-0091-82 | Stock = 0.2 mg/mL |
| anti-Sca1 (Ly6A/E) APC-Cy7 (clone: D7) | Biolegend | 108126 | Stock = 0.2 mg/mL |
| anti-α7 integrin PE (clone: R2F2)) | UBC AbLab | 67-0010-05 | Stock = 1 mg/mL |
| BD FACS Aria III (4 laser) instrument | BD Biosciences | N/A | 405, 488, 561, and 633 nm laser |
| Bovine Serum Albumin | Sigma Aldrich | A7030-50G | |
| Buprenorphine 0.3 mg/mL | Ceva | Vnr 054594 | |
| CD104 (Clone: 346-11A) | BD Biosciences | 553745 | Dy162; In-house conjugated |
| CD106/VCAM-1 (Clone: 429 MVCAM.A) | Biolegend | 105701 | Er170; In-house conjugated |
| CD11b (Clone: M1/70) | BD Biosciences | 553308 | Nd148; In-house conjugated |
| CD29/Integrin β1 (Clone: 9EG7) | BD Biosciences | 553715 | Tm169; In-house conjugated |
| CD31 (Clone: MEC 13.3) | BD Biosciences | 557355 | Sm154; In-house conjugated |
| CD34 (Clone: RAM34) | BD Biosciences | 551387 | Lu175; In-house conjugated |
| CD44 (Clone: IM7) | BD Biosciences | 550538 | Yb171; In-house conjugated |
| CD45 (Clone: MEC 30-F11) | BD Biosciences | 550539 | Sm147; In-house conjugated |
| CD9 (Clone: KMC8) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 14-0091-85 | Yb174; In-house conjugated |
| CD90.2/Thy1.2 (Clone: 30-H12) | BD Biosciences | 553009 | Nd144; In-house conjugated |
| CD98 (Clone: H202-141) | BD Biosciences | 557479 | Pr141; In-house conjugated |
| Cell Acquisition Solution/Maxpar CAS-buffer | Standard Biotools | 201240 | |
| Cell-ID Intercalator-Iridium | Standard Biotools | 201192B | cationic nucleic acid intercalator |
| Cisplatin | Merck | P4394 | Pt195 |
| Cisplatin (cis-Diammineplatinum(II) dichloride) | Merck | P4394 | |
| Clear 1.5 mL tube | Fisher Scientific | 11926955 | |
| Collagenase, Type II | Worthington Biochemical Corporation | LS004177 | |
| Counting chamber | Merck | BR718620-1EA | |
| CXCR4/SDF1 (Clone: 2B11/CXCR4 ) | BD Biosciences | 551852 | Gd158; In-house conjugated |
| DAPI (1 mg/mL) | BD Biosciences | 564907 | |
| Dark 1.5 mL tube | Fisher Scientific | 15386548 | |
| Dispase II | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 17105041 | |
| Dissection Scissors | Fine Science Tools | 14568-09 | |
| DMEM (low glucose, with pyruvate) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11885-092 | |
| EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt) | Merck | E5134 | Na2EDTA-2H20 |
| EQ Four Element Calibration Beads (EQ beads) | Standard Biotools | 201078 | Calibration beads |
| Fetal Bovine Serum, qualified, Brazil origin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 10270106 | |
| Forceps Dumont #5SF | Fine Science Tools | 11252-00 | |
| Forceps Dumont #7 | Hounisen.com | 1606.3350 | |
| Goat serum | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 16210-072 | |
| Helios CyTOF system | Standard Biotools | N/A | |
| Horse Serum, heat inactivated, New Zealand origin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 26-050-088 | |
| IdU | Merck | I7125 | I127 |
| Iridium-Intercalator | Standard Biotools | 201240 | Ir191/193 |
| Isoflurane/Attane Vet | ScanVet | Vnr 055226 | |
| Methanol | Fisher Scientific | M/3900/17 | |
| Myf5 (Clone: C-20) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Sc-302 | Yb173; In-house conjugated |
| MyoD (Clone: 5.8A) | BD Biosciences | 554130 | Dy164; In-house conjugated |
| MyoG (Clone: F5D) | BD Biosciences | 556358 | Gd160; In-house conjugated |
| Nalgene Rapid-Flow Sterile Disposable Bottle Top 0.20 μM PES Filters | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 595-4520 | |
| Notexin | Latoxan | L8104 | Resuspend to 50 µg/ml in sterile PBS. Keep stocks (e.g. 50 µl) at -20 °C |
| Nutrient mixture F-10 (Ham's) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 31550031 | |
| pAkt (Clone: D9E) | Standard Biotools | 3152005A | Sm152 |
| Pax7 (Clone: PAX7) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Sc-81648 | Eu153; In-house conjugated |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin (10,000 U/mL) (Pen/Strep) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15140122 | |
| PES Filter Units 0.20 μM | Fisher Scientific | 15913307 | |
| PES Syringe Filter | Fisher Scientific | 15206869 | |
| Petri dish | Sarstedt | 82.1472.001 | |
| PFA 16% EM grade | MP Biomedicals | 219998320 | |
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | Fisher Scientific | 10375810 | |
| Potassium phosphate, monobasic, anhydrous (KH2PO4) | Fisher Scientific | 10573181 | |
| pRb (Clone: J112-906) | Standard Biotools | 3166011A | Er166 |
| pS6 kinase (Clone: N7-548) | Standard Biotools | 3172008A | Yb172 |
| Sca-1 (Clone: E13-161.7) | BD Biosciences | 553333 | Nd142; In-house conjugated |
| Sodium Azide | Sigma Aldrich | S2002 | |
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | Fisher Scientific | 10553515 | |
| Sodium phosphate, dibasic, heptahydrate (Na2HPO4-6H2O) | Merck | S9390 | |
| Sterile saline solution 0.9% | Fresenius | B306414/02 | |
| α7 integrin (Clone: 3C12) | MBL international | K0046-3 | Ho165; In-house conjugated |
References
- Mukund, K., Subramaniam, S. Skeletal muscle: A review of molecular structure and function in health and disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 12 (1), e1462 (2020).
- Feige, P., Brun, C. E., Ritso, M., Rudnicki, M. A. Orienting muscle stem cells for regeneration in homeostasis, aging, and disease. Cell Stem Cell. 23 (5), 653-664 (2018).
- Mauro, A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 9 (2), 493-495 (1961).
- Seale, P., et al. Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell. 102 (6), 777-786 (2000).
- Fuchs, E., Blau, H. M. Tissue stem cells: Architects of their niches. Cell Stem Cell. 27 (4), 532-556 (2020).
- Hernández-hernández, J. M., et al. The myogenic regulatory factors, determinants of muscle development, cell identity and regeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 72, 10-18 (2017).
- Zammit, P. S. Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 72, 19-32 (2017).
- Sabourin, L. A. The molecular regulation of myogenesis. Clin Genet. 57 (1), 16-25 (2000).
- Cooper, R. N., et al. In vivo satellite cell activation via Myf5 and MyoD in regenerating mouse skeletal muscle. J Cell Sci. 112 (17), 2895-2901 (1999).
- Rudnicki, M. A., Jaenisch, R. The MyoD family of transcription factors and skeletal myogenesis. Bioessays. 17 (3), 203-209 (1995).
- Braun, T., Arnold, H. H. Inactivation of Myf-6 and Myf-5 genes in mice leads to alterations in skeletal muscle development. EMBO J. 14 (6), 1176-1186 (1995).
- Yablonka-Reuveni, Z. Development and postnatal regulation of adult myoblasts. Microsc Res Tech. 30 (5), 366-380 (1995).
- Braun, T., et al. MyoD expression marks the onset of skeletal myogenesis in Myf-5 mutant mice. Development. 120 (11), 3083-3092 (1994).
- Rudnicki, M. A., et al. MyoD or Myf-5 is required for the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell. 75 (7), 1351-1359 (1993).
- Montarras, D., et al. Developmental biology: Direct isolation of satellite cells for skeletal muscle regeneration. Science. 309 (5743), 2064-2067 (2005).
- Sacco, A., Doyonnas, R., Kraft, P., Vitorovic, S., Blau, H. M. Self-renewal and expansion of single transplanted muscle stem cells. Nature. 456 (7221), 502-506 (2008).
- Cerletti, M., et al. Highly efficient, functional engraftment of skeletal muscle stem cells in dystrophic muscles. Cell. 134 (1), 37-47 (2008).
- Liu, L., Cheung, T. H., Charville, G. W., Rando, T. A. Isolation of skeletal muscle stem cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Nat Protoc. 10 (10), 1612-1624 (2015).
- Porpiglia, E., et al. High-resolution myogenic lineage mapping by single-cell mass cytometry. Nat Cell Biol. 19 (5), 558-567 (2017).
- Behbehani, G. K., Bendall, S. C., Clutter, M. R., Fantl, W. J., Nolan, G. P. Single-cell mass cytometry adapted to measurements of the cell cycle. Cytometry Part A. 81 (7), 552-566 (2012).
- Hartmann, F. J., et al. . Mass Cytometry: Methods and Protocols. , (2019).
- Devine, R. D., Behbehani, G. K. Use of the pyrimidine analog, 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine (IdU) with cell cycle markers to establish cell cycle phases in a mass cytometry platform. J Vis Exp. (176), e60556 (2021).
- Bendall, S. C., et al. Single-cell mass cytometry of differential immune and drug responses across a human hematopoietic continuum. Science. 332 (6030), 687-696 (2011).
- Nag, A. C., Foster, J. D. Myogenesis in adult mammalian skeletal muscle in vitro. J Anat. 132, 1-18 (1981).
- Le Moigne, A., et al. Characterization of myogenesis from adult satellite cells cultured in vitro). Int J Dev Biol. 34, 171-180 (1990).
- Yablonka-Reuveni, Z. Development and postnatal regulation of adult myoblasts. Microsc Res Tech. 30 (5), 366-380 (1995).
- Chu, C., Cogswell, J., Kohtz, D. S. MyoD functions as a transcriptional repressor in proliferating myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 272 (6), 3145-3148 (1997).
- Shah, B., Hyde-Dunn, J., Jones, G. E. Proliferation of murine myoblasts as measured by bromodeoxyuridine incorporation. Methods in Mol Biol. 75, 349-355 (1997).
- Springer, M. L., Blau, H. M. High-efficiency retroviral infection of primary myoblasts. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 23 (3), 203-209 (1997).
- Rando, T. A., Blau, H. M. Primary mouse myoblast purification, characterization, and transplantation for cell-mediated gene therapy. J Cell Biol. 125 (6), 1275-1287 (1994).
- Springer, M. L., Rando, T. A., Blau, H. M. Gene delivery to muscle. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. , (2002).
- Cull-Candy, S. G., Fohlman, J., Gustavsson, D., Lullmann-Rauch, R., Thesleff, S. The effects of taipoxin and notexin on the function and fine structure of the murine neuromuscular junction. Neuroscience. 1 (3), 175-180 (1976).
- Francis, B., John, T. R., Seebart, C., Kaiser, I. I. New toxins from the venom of the common tiger snake (Notechis scutatus scutatus). Toxicon. 29 (1), 85-96 (1991).
- Navarro, K. L., Huss, M., Smith, J. C., Sharp, P., Marx, J. O., Pacharinsak, C. Mouse Anesthesia: The Art and Science. ILAR Journal. 62, 238-273 (2021).
- Langford, D., Bailey, A., Chanda, M., et al. Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse. Nat Methods. 7, 447-449 (2010).
- Matsumiya, L. C., Sorge, R. E., Sotocinal, S. G., Tabaka, J. M., Wieskopf, J. S., Zaloum, A., King, O. D., Mogil, J. S. Using the Mouse Grimace Scale to reevaluate the efficacy of postoperative analgesics in laboratory mice. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2012 (1), 42-49 (2012).
- Gonzalez, V. D., et al. High-grade serous ovarian tumor cells modulate NK cell function to create an immune-tolerant microenvironment. Cell Rep. 36 (9), 109632 (2021).
- Delgado-Gonzalez, A., et al. Measuring trogocytosis between ovarian tumor and natural killer cells. STAR Protoc. 3 (2), 101425 (2022).
- Finck, R., et al. Normalization of mass cytometry data with bead standards. Cytometry Part A. 83 (5), 483-494 (2013).
- Leipold, M. D., Maecker, H. T. Mass cytometry: protocol for daily tuning and running cell samples on a CyTOF mass cytometer. J Vis Exp. (69), e4398 (2012).
- McCarthy, R. L., Duncan, A. D., Barton, M. C. Sample preparation for mass cytometry analysis. J Vis Exp. (122), e54394 (2017).
- Kotecha, N., Krutzik, P. O., Irish, J. M. Web-based analysis and publication of flow cytometry experiments. Curr Protoc Cytom. , (2010).
- Fienberg, H. G., Simonds, E. F., Fantl, W. J., Nolan, G. P., Bodenmiller, B. A platinum-based covalent viability reagent for single-cell mass cytometry. Cytometry Part A. 81 (6), 467-475 (2012).
- Kimball, A. K., et al. A beginner's guide to analyzing and visualizing mass cytometry data. J Immunol. 200 (1), 3-22 (2018).
- Weber, L. M., Robinson, M. D. Comparison of clustering methods for high-dimensional single-cell flow and mass cytometry data. Cytometry Part A. 89 (12), 1084-1096 (2016).
- Samusik, N., Good, Z., Spitzer, M. H., Davis, K. L., Nolan, G. P. Automated mapping of phenotype space with single-cell data. Nat Methods. 13 (6), 493-496 (2016).
- Ornatsky, O. I., et al. Study of cell antigens and intracellular DNA by identification of element-containing labels and metallointercalators using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 80 (7), 2539-2547 (2008).
- Relaix, F., et al. Perspectives on skeletal muscle stem cells. Nat Commun. 12 (1), 692 (2021).
- de Morree, A., et al. Staufen1 inhibits MyoD translation to actively maintain muscle stem cell quiescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 114 (43), E8996-E9005 (2017).
- Luo, D., et al. Deltex2 represses MyoD expression and inhibits myogenic differentiation by acting as a negative regulator of Jmjd1c. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 114 (15), E3071-E3080 (2017).
- Wersto, R. P., et al. Doublet discrimination in DNA cell-cycle analysis. Cytometry. 46 (5), 296-306 (2001).
- Porpiglia, E., Blau, H. M. Plasticity of muscle stem cells in homeostasis and aging. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 77, 101999 (2022).
- Porpiglia, E., et al. Elevated CD47 is a hallmark of dysfunctional aged muscle stem cells that can be targeted to augment regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 29 (12), 1653-1668 (2022).
- Brunet, A., Goodell, M. A., Rando, T. A. Ageing and rejuvenation of tissue stem cells and their niches. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 24 (1), 45-62 (2022).
- Danielli, S. G., et al. Single-cell profiling of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma reveals RAS pathway inhibitors as cell-fate hijackers with therapeutic relevance. Sci Adv. 9 (6), (2023).
- de Morree, A., Rando, T. A. Regulation of adult stem cell quiescence and its functions in the maintenance of tissue integrity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 24 (5), 334-354 (2023).
- Yucel, N., et al. Glucose metabolism drives histone acetylation landscape transitions that dictate muscle stem cell glucose metabolism drives histone acetylation landscape transitions that dictate muscle stem cell function. Cell Rep. 27 (13), 3939-3955 (2019).
- Tierney, M. T., Sacco, A. Inducing and evaluating skeletal muscle injury by notexin and barium chloride. Methods Mol Biol. 1460, 53-60 (2016).
- Hardy, D., et al. Comparative study of injury models for studying muscle regeneration in mice. PLoS One. 11 (1), e0147198 (2016).
- Call, J. A., Lowe, D. A. Eccentric contraction-induced muscle injury: Reproducible, quantitative, physiological models to impair skeletal muscle's capacity to generate force. Methods Mol Biol. 1460, 3-18 (2016).
- Garry, G. A., Antony, M. L., Garry, D. J. Cardiotoxin Induced Injury and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Methods Mol Biol. 1460, 61-71 (2016).
- Le, G., Lowe, D. A., Kyba, M. Freeze injury of the tibialis anterior muscle. Methods Mol Biol. 1460, 33-41 (2016).
- Borok, M., et al. Progressive and coordinated mobilization of the skeletal muscle niche throughout tissue repair revealed by single-cell proteomic analysis. Cells. 10 (4), 744 (2021).
- Petrilli, L. L., et al. High-dimensional single-cell quantitative profiling of skeletal muscle cell population dynamics during regeneration. Cells. 9 (7), 1723 (2020).
- Giordani, L., et al. High-dimensional single-cell cartography reveals novel skeletal muscle-resident cell populations. Mol Cell. 74 (3), 609-621 (2019).
- Hartmann, F. J., et al. Scalable conjugation and characterization of immunoglobulins with stable mass isotope reporters for single-cell mass cytometry analysis. Methods Mol Biol. 1989, 55-81 (2019).
- Frimand, Z., Das Barman, S., Kjær, T. R., Porpiglia, E., de Morrée, A. Isolation of quiescent stem cell populations from individual skeletal muscles. J Vis Exp. (190), e64557 (2022).
- Krutzik, P. O., Nolan, G. P. Intracellular phospho-protein staining techniques for flow cytometry: monitoring single cell signaling events. Cytometry A. 55 (2), 61-70 (2003).
- Bodenmiller, B., et al. Multiplexed mass cytometry profiling of cellular states perturbed by small-molecule regulators. Nat Biotechnol. 30 (9), 858-867 (2012).
- Schulz, K. R., Danna, E. A., Krutzik, P. O., Nolan, G. P. Single-cell phospho-protein analysis by flow cytometry. Curr Protoc Immunol. , 11-20 (2012).
- Krutzik, P. O., Clutter, M. R., Nolan, G. P. Coordinate analysis of murine immune cell surface markers and intracellular phosphoproteins by flow cytometry. J Immunol. 175 (4), 2357-2365 (2005).
- Krutzik, P. O., Irish, J. M., Nolan, G. P., Perez, O. D. Analysis of protein phosphorylation and cellular signaling events by flow cytometry: techniques and clinical applications. Clin Immunol. 110 (3), 206-221 (2004).
- Han, G., Spitzer, M. H., Bendall, S. C., Fantl, W. J., Nolan, G. P. Metal-isotope-tagged monoclonal antibodies for high-dimensional mass cytometry. Nat Protoc. 13 (10), 2121-2148 (2018).
- Chevrier, S., et al. Compensation of signal spillover in suspension and imaging mass cytometry. Cell Syst. 6 (5), 612-620 (2018).
- Bjornson, Z. B., Nolan, G. P., Fantl, W. J. Single-cell mass cytometry for analysis of immune system functional states. Curr Opin Immunol. 25 (4), 484-494 (2013).
- Kalina, T., Lundsten, K., Engel, P. Relevance of antibody validation for flow cytometry. Cytometry A. 97 (2), 126-136 (2020).
- Baumgarth, N., Roederer, M. A practical approach to multicolor flow cytometry for immunophenotyping. J Immunol Methods. 243 (1-2), 77-97 (2000).
- Roederer, M. Spectral compensation for flow cytometry: visualization artifacts, limitations, and caveats. Cytometry. 45 (3), 194-205 (2001).
- Tung, J. W., Parks, D. R., Moore, W. A., Herzenberg, L. A., Herzenberg, L. A. New approaches to fluorescence compensation and visualization of FACS data. Clin Immunol. 110 (3), 277-283 (2004).
- Cossarizza, A., et al. Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (third edition). Eur J Immunol. 51 (12), 2708-3145 (2021).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved